URoboSim -- An Episodic Simulation Framework for Prospective Reasoning in Robotic Agents
Paper and Code
Dec 08, 2020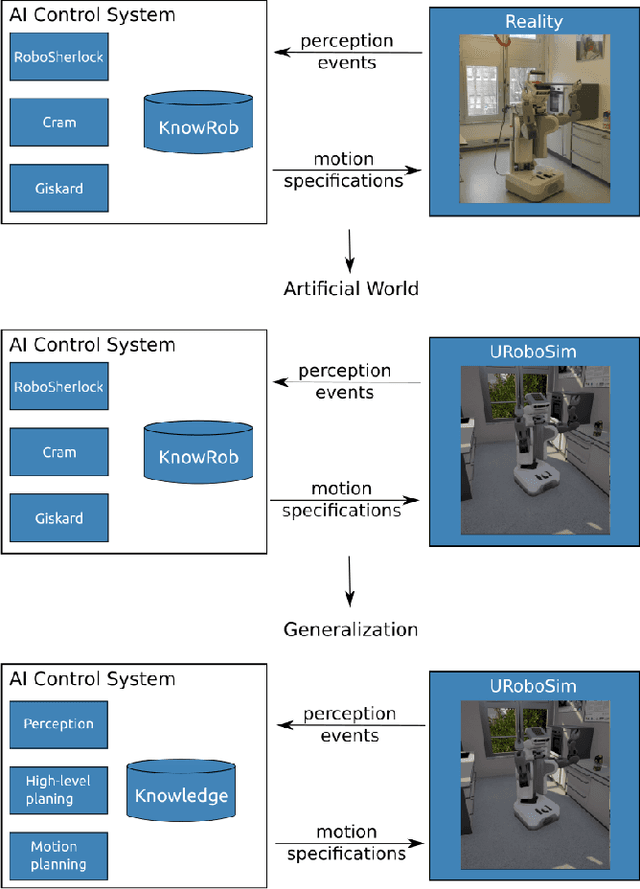
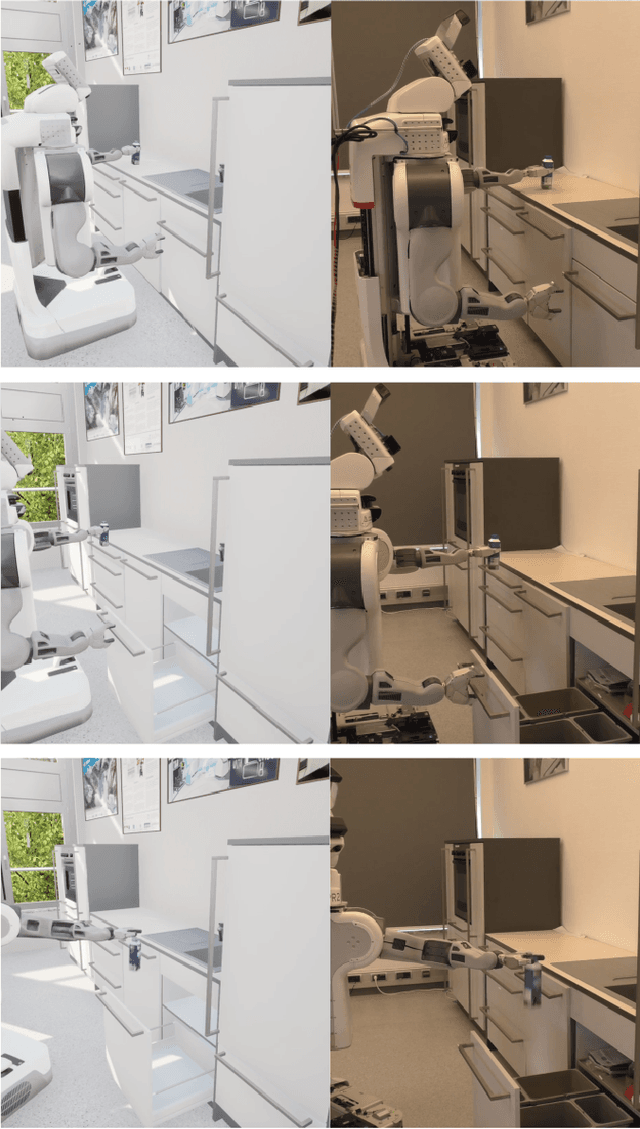

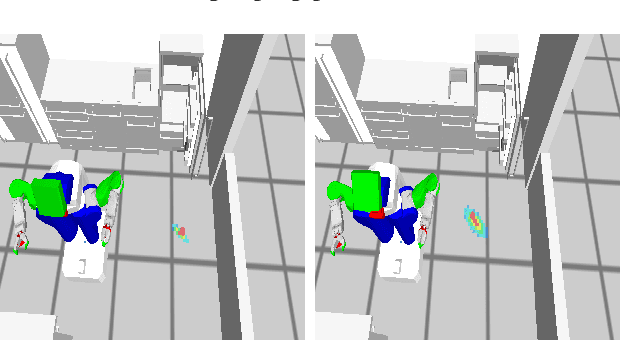
Anticipating what might happen as a result of an action is an essential ability humans have in order to perform tasks effectively. On the other hand, robots capabilities in this regard are quite lacking. While machine learning is used to increase the ability of prospection it is still limiting for novel situations. A possibility to improve the prospection ability of robots is through simulation of imagined motions and the physical results of these actions. Therefore, we present URoboSim, a robot simulator that allows robots to perform tasks as mental simulation before performing this task in reality. We show the capabilities of URoboSim in form of mental simulations, generating data for machine learning and the usage as belief state for a real robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge