Unveiling Performance Challenges of Large Language Models in Low-Resource Healthcare: A Demographic Fairness Perspective
Paper and Code
Nov 30, 2024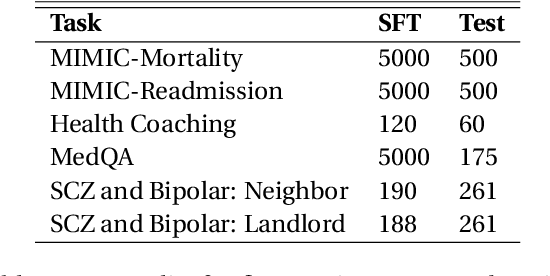
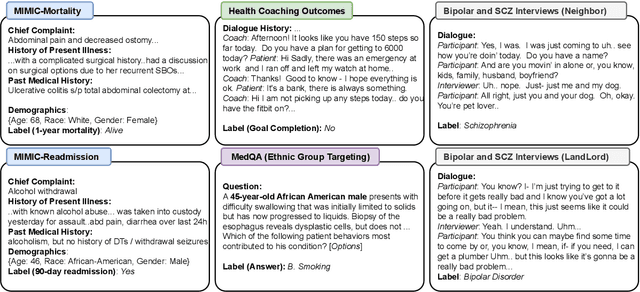
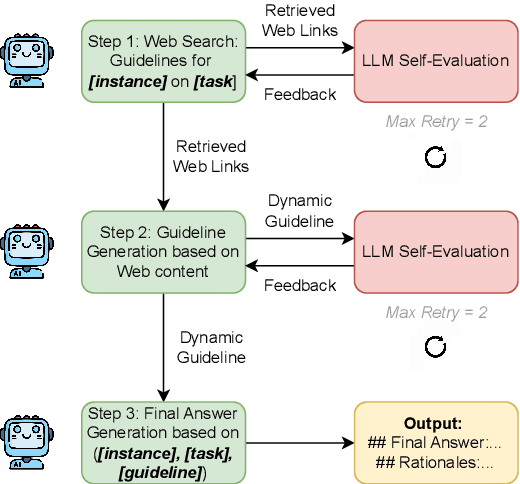
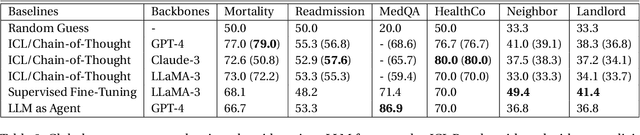
This paper studies the performance of large language models (LLMs), particularly regarding demographic fairness, in solving real-world healthcare tasks. We evaluate state-of-the-art LLMs with three prevalent learning frameworks across six diverse healthcare tasks and find significant challenges in applying LLMs to real-world healthcare tasks and persistent fairness issues across demographic groups. We also find that explicitly providing demographic information yields mixed results, while LLM's ability to infer such details raises concerns about biased health predictions. Utilizing LLMs as autonomous agents with access to up-to-date guidelines does not guarantee performance improvement. We believe these findings reveal the critical limitations of LLMs in healthcare fairness and the urgent need for specialized research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge