Unsupervised Space-Time Clustering using Persistent Homology
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2019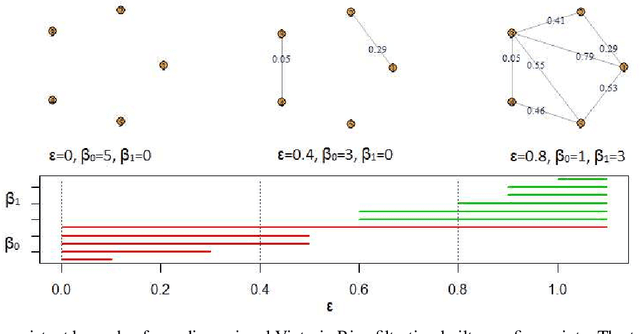
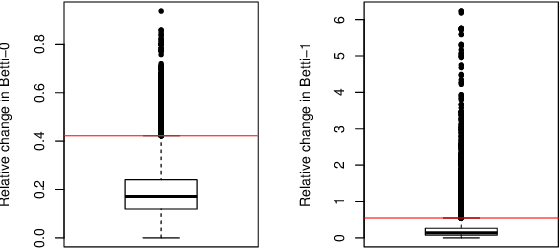
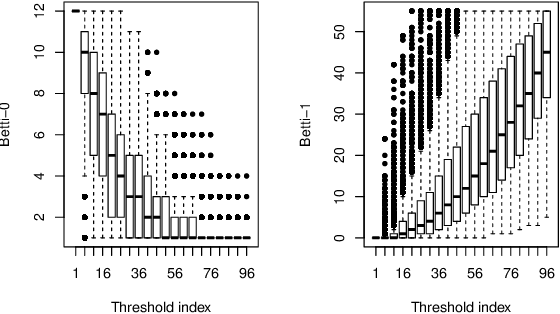
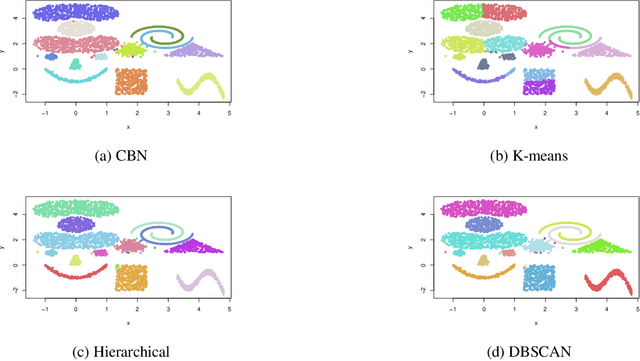
This paper presents a new clustering algorithm for space-time data based on the concepts of topological data analysis and in particular, persistent homology. Employing persistent homology - a flexible mathematical tool from algebraic topology used to extract topological information from data - in unsupervised learning is an uncommon and a novel approach. A notable aspect of this methodology consists in analyzing data at multiple resolutions which allows to distinguish true features from noise based on the extent of their persistence. We evaluate the performance of our algorithm on synthetic data and compare it to other well-known clustering algorithms such as K-means, hierarchical clustering and DBSCAN. We illustrate its application in the context of a case study of water quality in the Chesapeake Bay.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge