Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation via Pre-trained StyleGAN2 Network
Paper and Code
Oct 27, 2020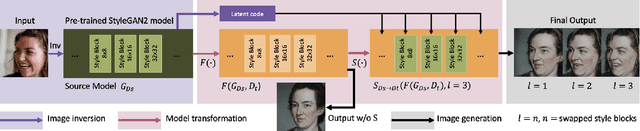
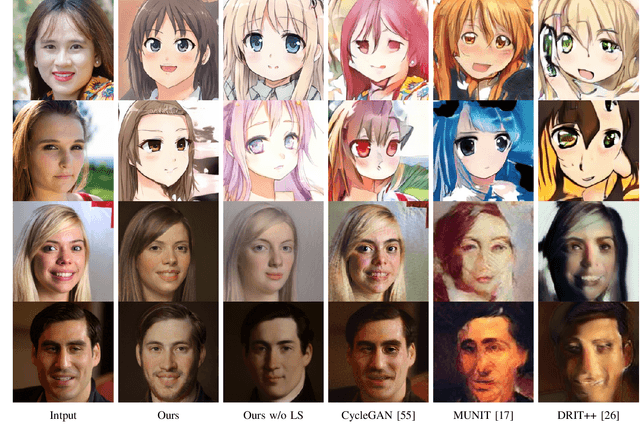
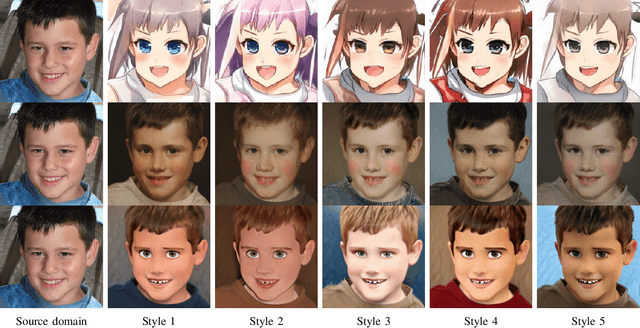

Image-to-Image (I2I) translation is a heated topic in academia, and it also has been applied in real-world industry for tasks like image synthesis, super-resolution, and colorization. However, traditional I2I translation methods train data in two or more domains together. This requires lots of computation resources. Moreover, the results are of lower quality, and they contain many more artifacts. The training process could be unstable when the data in different domains are not balanced, and modal collapse is more likely to happen. We proposed a new I2I translation method that generates a new model in the target domain via a series of model transformations on a pre-trained StyleGAN2 model in the source domain. After that, we proposed an inversion method to achieve the conversion between an image and its latent vector. By feeding the latent vector into the generated model, we can perform I2I translation between the source domain and target domain. Both qualitative and quantitative evaluations were conducted to prove that the proposed method can achieve outstanding performance in terms of image quality, diversity and semantic similarity to the input and reference images compared to state-of-the-art works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge