Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in 3D Brain MRI using Deep Learning with impured training data
Paper and Code
Apr 12, 2022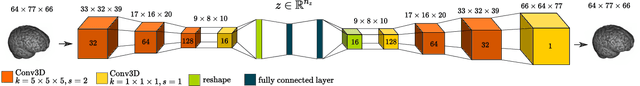
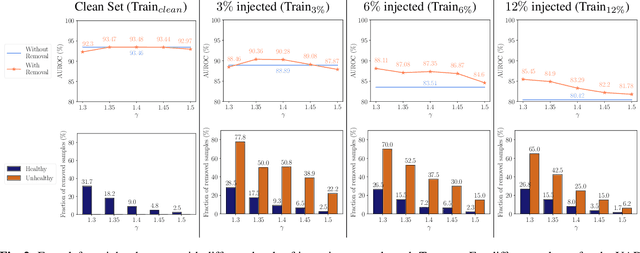
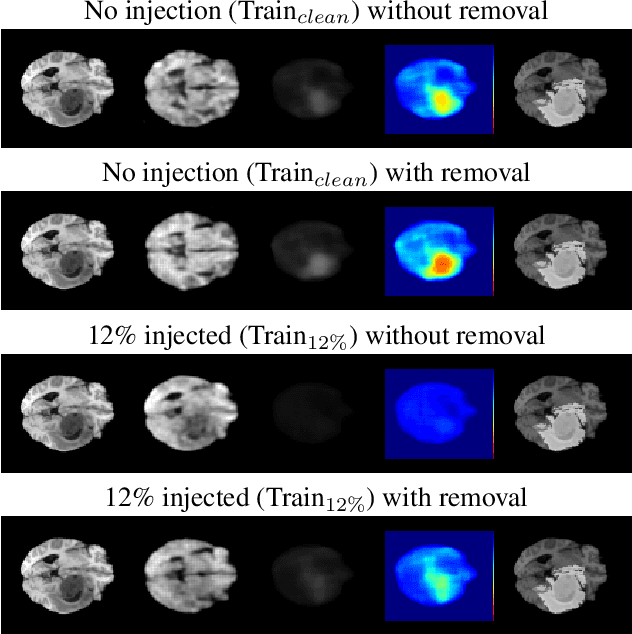
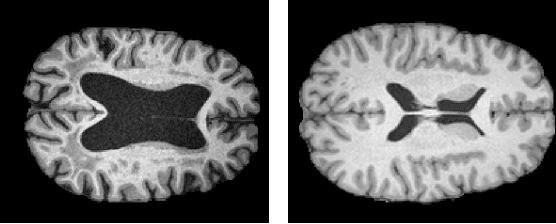
The detection of lesions in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-scans of human brains remains challenging, time-consuming and error-prone. Recently, unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) methods have shown promising results for this task. These methods rely on training data sets that solely contain healthy samples. Compared to supervised approaches, this significantly reduces the need for an extensive amount of labeled training data. However, data labelling remains error-prone. We study how unhealthy samples within the training data affect anomaly detection performance for brain MRI-scans. For our evaluations, we consider three publicly available data sets and use autoencoders (AE) as a well-established baseline method for UAD. We systematically evaluate the effect of impured training data by injecting different quantities of unhealthy samples to our training set of healthy samples from T1-weighted MRI-scans. We evaluate a method to identify falsely labeled samples directly during training based on the reconstruction error of the AE. Our results show that training with impured data decreases the UAD performance notably even with few falsely labeled samples. By performing outlier removal directly during training based on the reconstruction-loss, we demonstrate that falsely labeled data can be detected and removed to mitigate the effect of falsely labeled data. Overall, we highlight the importance of clean data sets for UAD in brain MRI and demonstrate an approach for detecting falsely labeled data directly during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge