Unlocking Efficiency: Adaptive Masking for Gene Transformer Models
Paper and Code
Aug 13, 2024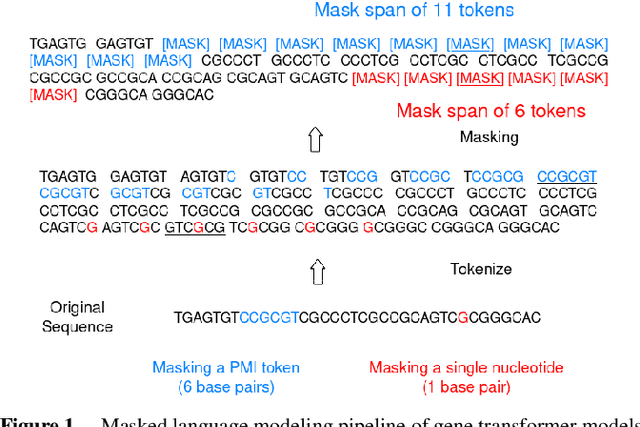
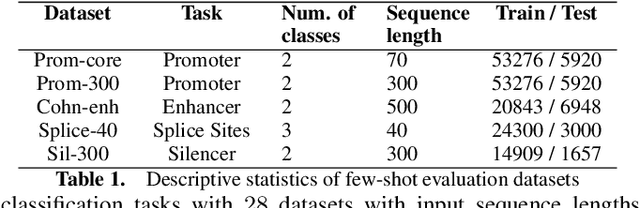
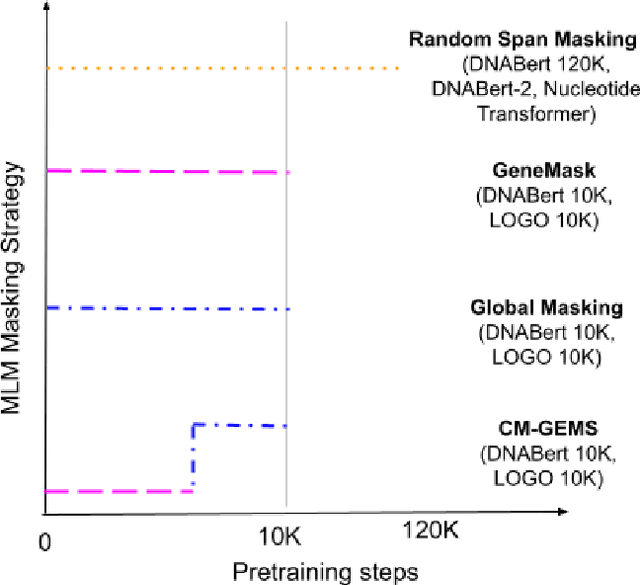
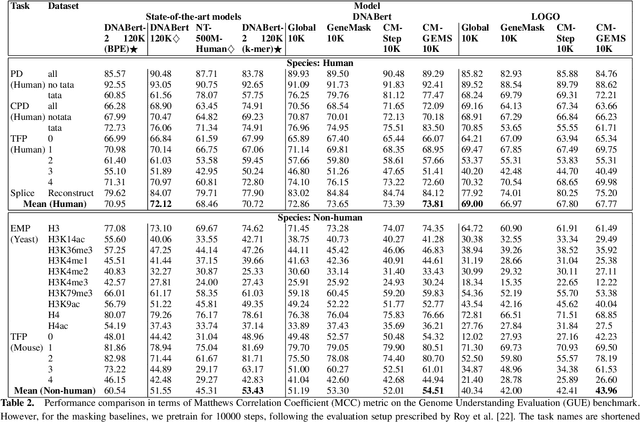
Gene transformer models such as Nucleotide Transformer, DNABert, and LOGO are trained to learn optimal gene sequence representations by using the Masked Language Modeling (MLM) training objective over the complete Human Reference Genome. However, the typical tokenization methods employ a basic sliding window of tokens, such as k-mers, that fail to utilize gene-centric semantics. This could result in the (trivial) masking of easily predictable sequences, leading to inefficient MLM training. Time-variant training strategies are known to improve pretraining efficiency in both language and vision tasks. In this work, we focus on using curriculum masking where we systematically increase the difficulty of masked token prediction task by using a Pointwise Mutual Information-based difficulty criterion, as gene sequences lack well-defined semantic units similar to words or sentences of NLP domain. Our proposed Curriculum Masking-based Gene Masking Strategy (CM-GEMS) demonstrates superior representation learning capabilities compared to baseline masking approaches when evaluated on downstream gene sequence classification tasks. We perform extensive evaluation in both few-shot (five datasets) and full dataset settings (Genomic Understanding Evaluation benchmark consisting of 27 tasks). Our findings reveal that CM-GEMS outperforms state-of-the-art models (DNABert-2, Nucleotide transformer, DNABert) trained at 120K steps, achieving similar results in just 10K and 1K steps. We also demonstrate that Curriculum-Learned LOGO (a 2-layer DNABert-like model) can achieve nearly 90% of the state-of-the-art model performance of 120K steps. We will make the models and codes publicly available at https://github.com/roysoumya/curriculum-GeneMask.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge