Universal Approximation Property of Hamiltonian Deep Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Mar 21, 2023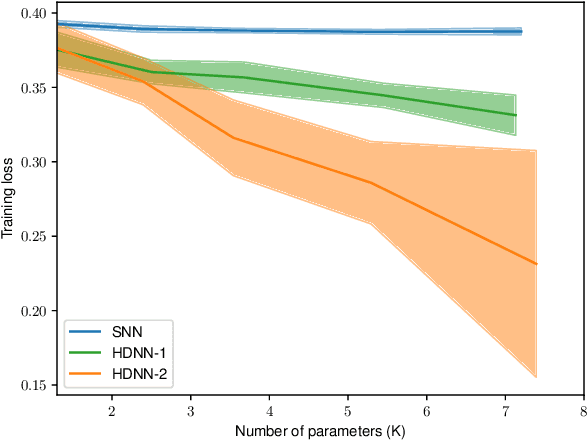
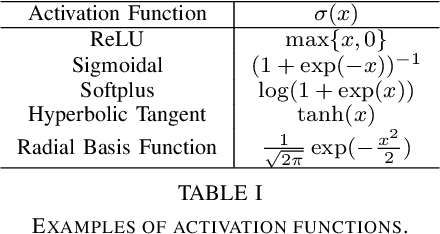
This paper investigates the universal approximation capabilities of Hamiltonian Deep Neural Networks (HDNNs) that arise from the discretization of Hamiltonian Neural Ordinary Differential Equations. Recently, it has been shown that HDNNs enjoy, by design, non-vanishing gradients, which provide numerical stability during training. However, although HDNNs have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in several applications, a comprehensive study to quantify their expressivity is missing. In this regard, we provide a universal approximation theorem for HDNNs and prove that a portion of the flow of HDNNs can approximate arbitrary well any continuous function over a compact domain. This result provides a solid theoretical foundation for the practical use of HDNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge