Unifying Optimization Methods for Color Filter Design
Paper and Code
Jun 24, 2020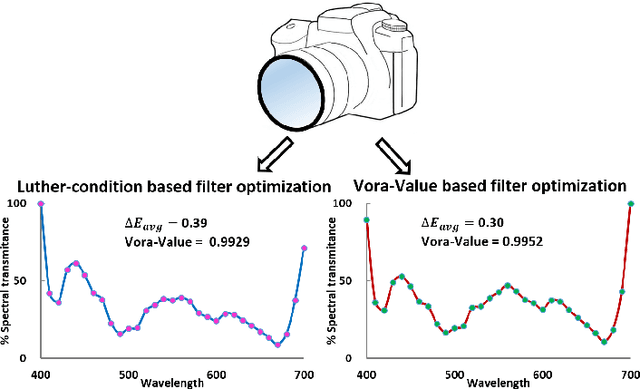
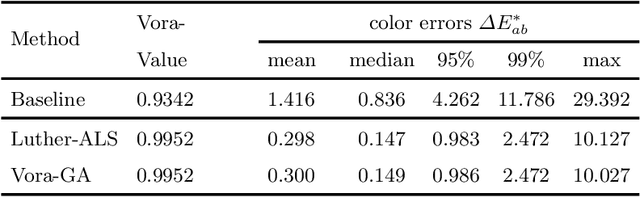
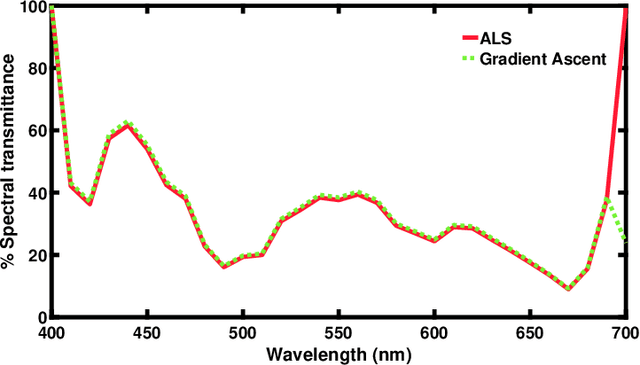
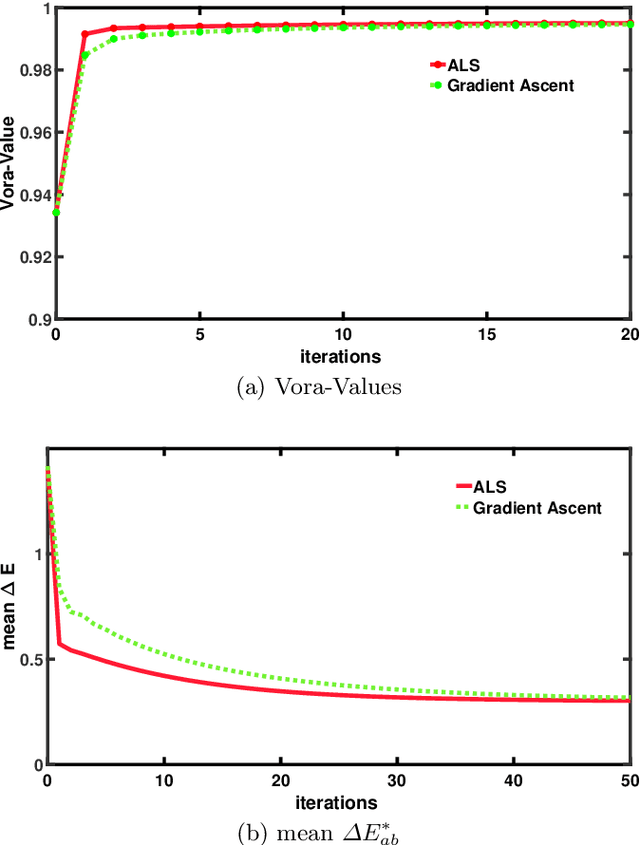
Through optimization we can solve for a filter that when the camera views the world through this filter, it is more colorimetric. Previous work solved for the filter that best satisfied the Luther condition: the camera spectral sensitivities after filtering were approximately a linear transform from the CIE XYZ color matching functions. A more recent method optimized for the filter that maximized the Vora-Value (a measure which relates to the closeness of the vector spaces spanned by the camera sensors and human vision sensors). The optimized Luther- and Vora-filters are different from one another. In this paper we begin by observing that the function defining the Vora-Value is equivalent to the Luther-condition optimization if we use the orthonormal basis of the XYZ color matching functions, i.e. we linearly transform the XYZ sensitivities to a set of orthonormal basis. In this formulation, the Luther-optimization algorithm is shown to almost optimize the Vora-Value. Moreover, experiments demonstrate that the modified orthonormal Luther-method finds the same color filter compared to the Vora-Value filter optimization. Significantly, our modified algorithm is simpler in formulation and also converges faster than the direct Vora-Value method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge