Underestimation of lung regions on chest X-ray segmentation masks assessed by comparison with total lung volume evaluated on computed tomography
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2024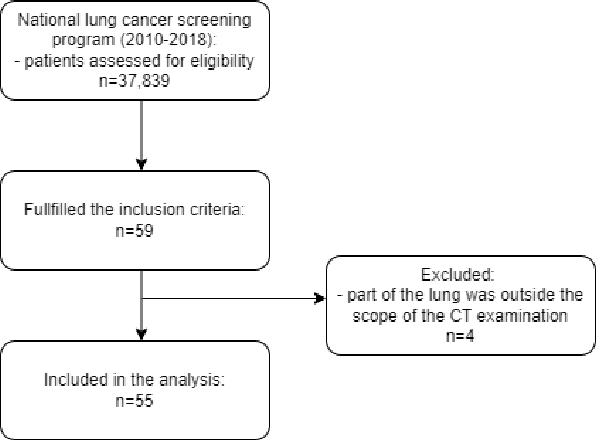
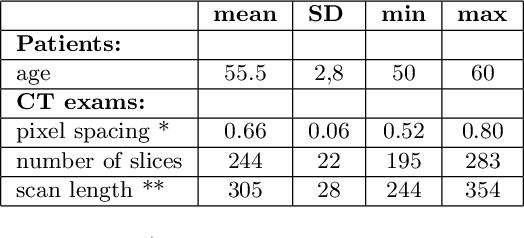
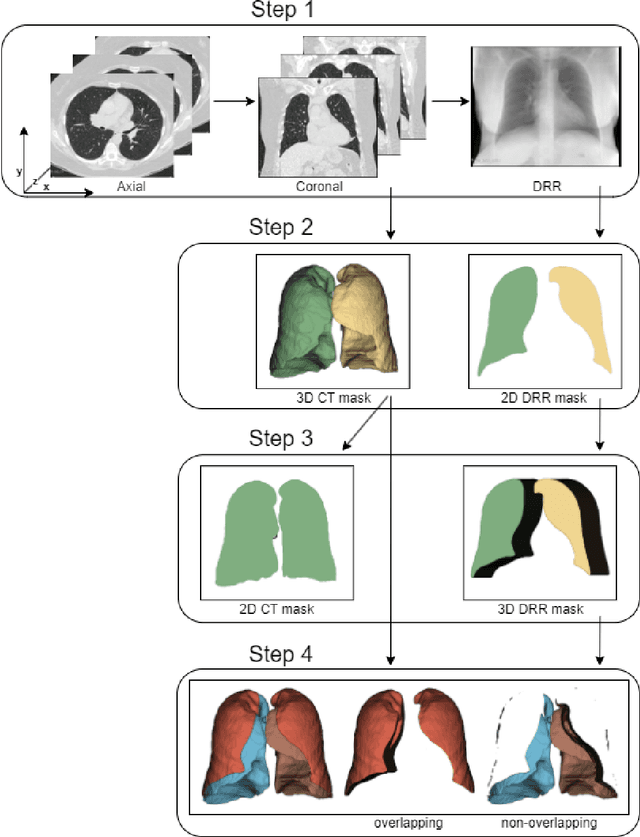
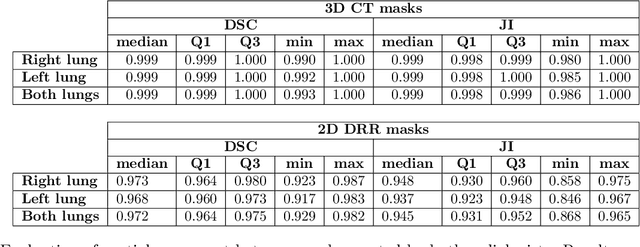
Lung mask creation lacks well-defined criteria and standardized guidelines, leading to a high degree of subjectivity between annotators. In this study, we assess the underestimation of lung regions on chest X-ray segmentation masks created according to the current state-of-the-art method, by comparison with total lung volume evaluated on computed tomography (CT). We show, that lung X-ray masks created by following the contours of the heart, mediastinum, and diaphragm significantly underestimate lung regions and exclude substantial portions of the lungs from further assessment, which may result in numerous clinical errors.
* Preprint to Elsevier
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge