Transfer Learning for Unseen Robot Detection and Joint Estimation on a Multi-Objective Convolutional Neural Network
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2018
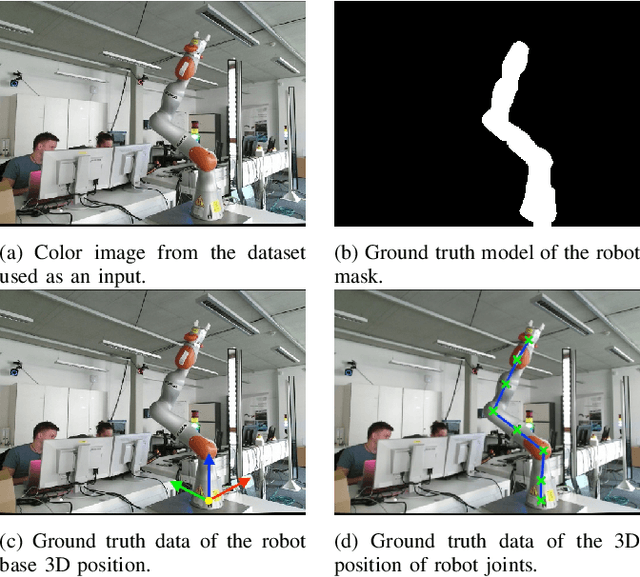

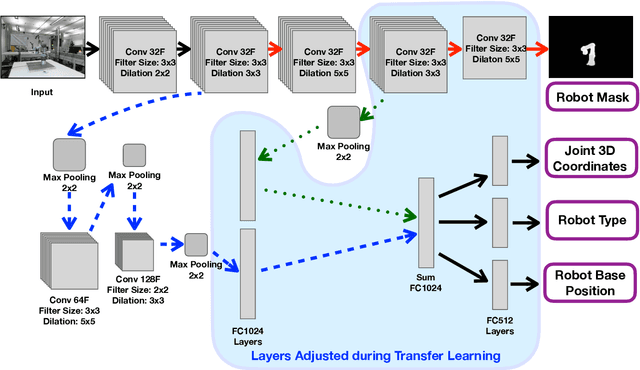
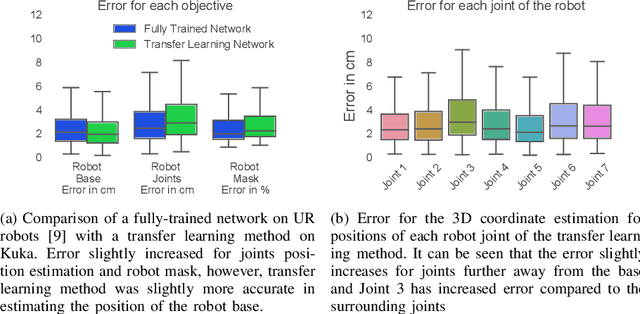
A significant problem of using deep learning techniques is the limited amount of data available for training. There are some datasets available for the popular problems like item recognition and classification or self-driving cars, however, it is very limited for the industrial robotics field. In previous work, we have trained a multi-objective Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to identify the robot body in the image and estimate 3D positions of the joints by using just a 2D image, but it was limited to a range of robots produced by Universal Robots (UR). In this work, we extend our method to work with a new robot arm - Kuka LBR iiwa, which has a significantly different appearance and an additional joint. However, instead of collecting large datasets once again, we collect a number of smaller datasets containing a few hundred frames each and use transfer learning techniques on the CNN trained on UR robots to adapt it to a new robot having different shapes and visual features. We have proven that transfer learning is not only applicable in this field, but it requires smaller well-prepared training datasets, trains significantly faster and reaches similar accuracy compared to the original method, even improving it on some aspects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge