Transfer Learning by Cascaded Network to identify and classify lung nodules for cancer detection
Paper and Code
Sep 24, 2020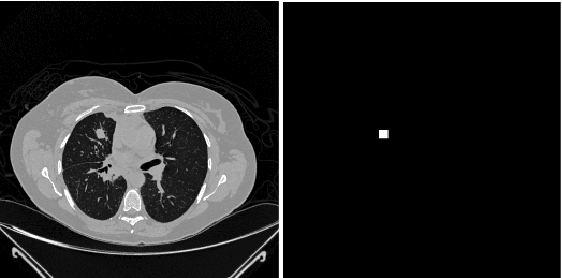

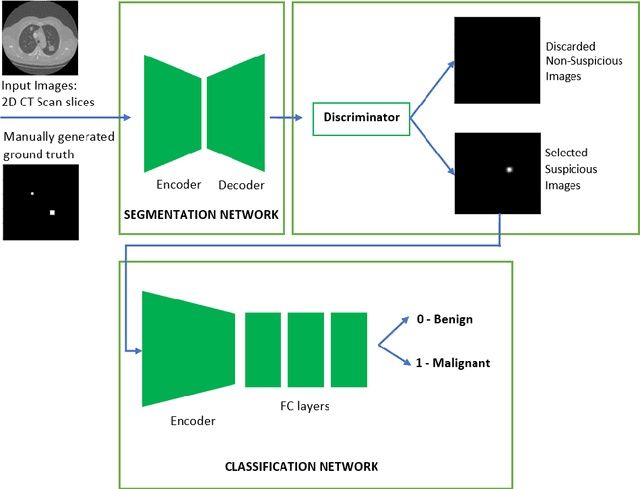

Lung cancer is one of the most deadly diseases in the world. Detecting such tumors at an early stage can be a tedious task. Existing deep learning architecture for lung nodule identification used complex architecture with large number of parameters. This study developed a cascaded architecture which can accurately segment and classify the benign or malignant lung nodules on computed tomography (CT) images. The main contribution of this study is to introduce a segmentation network where the first stage trained on a public data set can help to recognize the images which included a nodule from any data set by means of transfer learning. And the segmentation of a nodule improves the second stage to classify the nodules into benign and malignant. The proposed architecture outperformed the conventional methods with an area under curve value of 95.67\%. The experimental results showed that the classification accuracy of 97.96\% of our proposed architecture outperformed other simple and complex architectures in classifying lung nodules for lung cancer detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge