Transcribing Lyrics From Commercial Song Audio: The First Step Towards Singing Content Processing
Paper and Code
Apr 15, 2018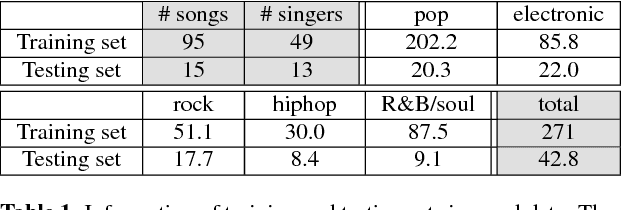
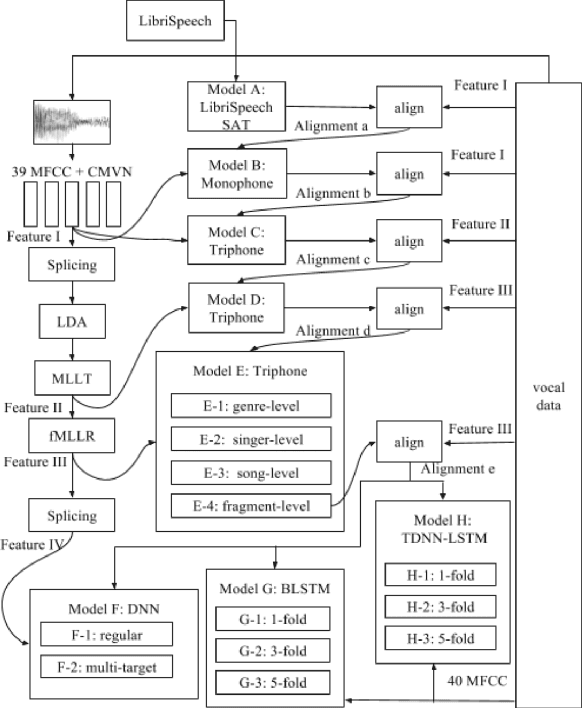
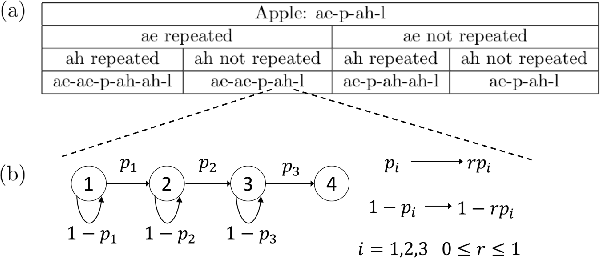
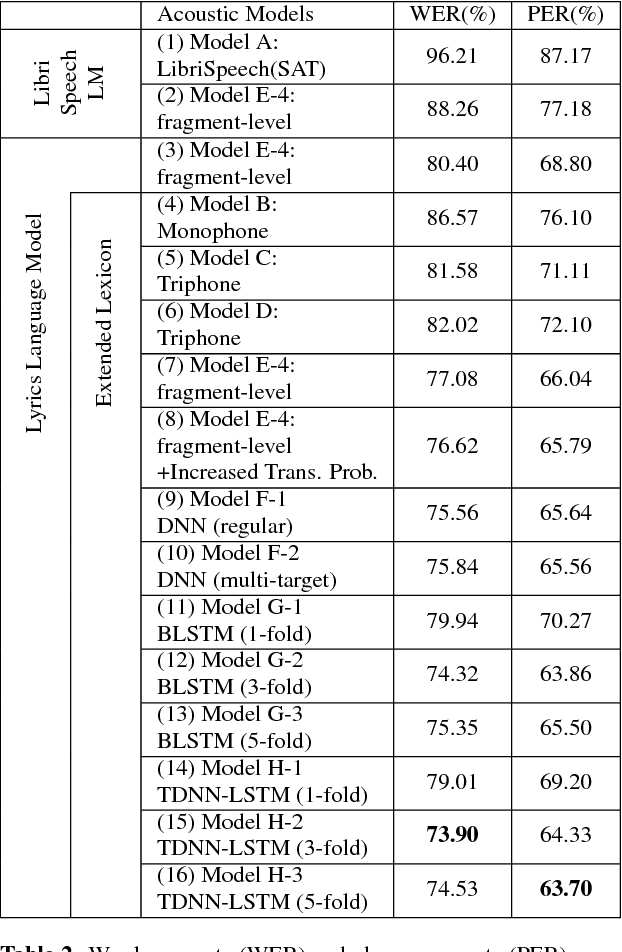
Spoken content processing (such as retrieval and browsing) is maturing, but the singing content is still almost completely left out. Songs are human voice carrying plenty of semantic information just as speech, and may be considered as a special type of speech with highly flexible prosody. The various problems in song audio, for example the significantly changing phone duration over highly flexible pitch contours, make the recognition of lyrics from song audio much more difficult. This paper reports an initial attempt towards this goal. We collected music-removed version of English songs directly from commercial singing content. The best results were obtained by TDNN-LSTM with data augmentation with 3-fold speed perturbation plus some special approaches. The WER achieved (73.90%) was significantly lower than the baseline (96.21%), but still relatively high.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge