Training neural network ensembles via trajectory sampling
Paper and Code
Sep 22, 2022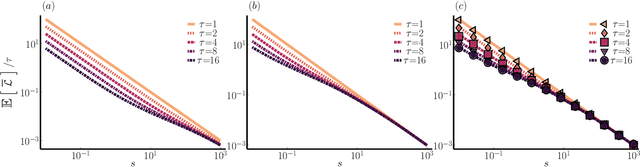
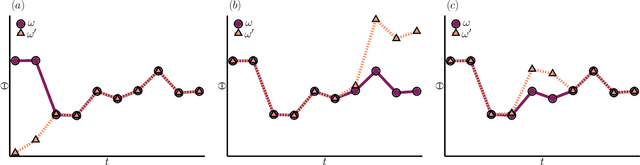
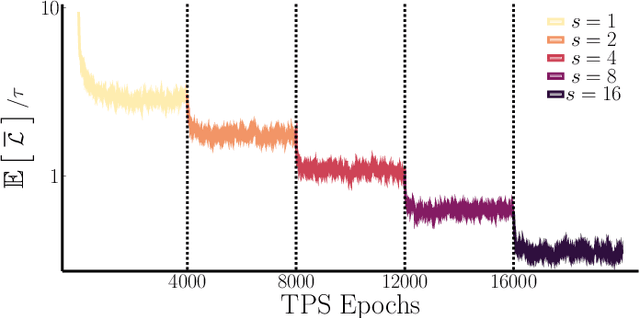
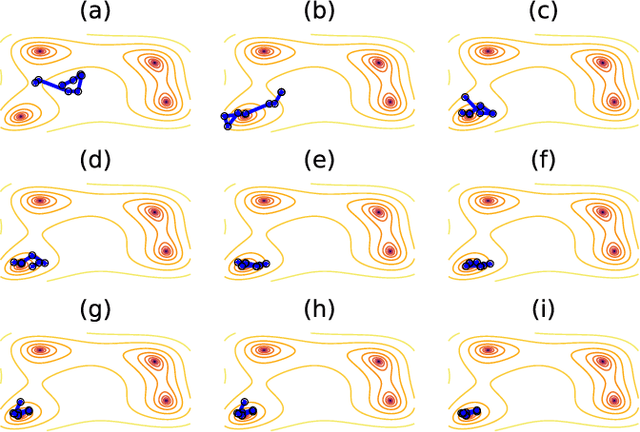
In machine learning, there is renewed interest in neural network ensembles (NNEs), whereby predictions are obtained as an aggregate from a diverse set of smaller models, rather than from a single larger model. Here, we show how to define and train a NNE using techniques from the study of rare trajectories in stochastic systems. We define an NNE in terms of the trajectory of the model parameters under a simple, and discrete in time, diffusive dynamics, and train the NNE by biasing these trajectories towards a small time-integrated loss, as controlled by appropriate counting fields which act as hyperparameters. We demonstrate the viability of this technique on a range of simple supervised learning tasks. We discuss potential advantages of our trajectory sampling approach compared with more conventional gradient based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge