Towards Unsupervised Dense Information Retrieval with Contrastive Learning
Paper and Code
Dec 16, 2021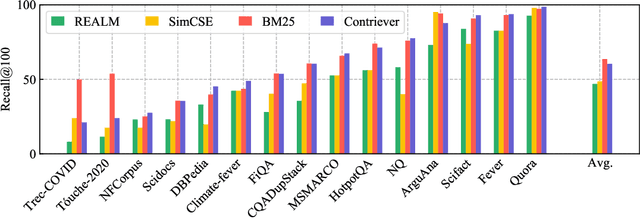
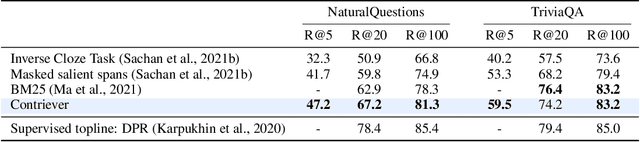
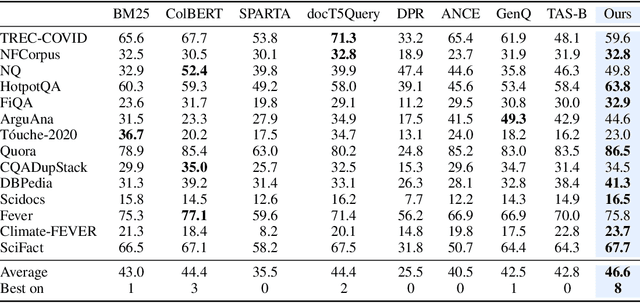
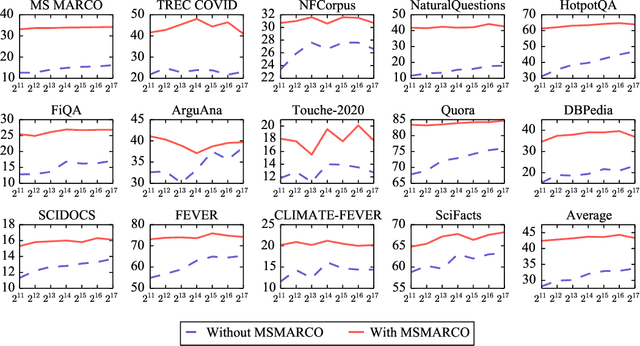
Information retrieval is an important component in natural language processing, for knowledge intensive tasks such as question answering and fact checking. Recently, information retrieval has seen the emergence of dense retrievers, based on neural networks, as an alternative to classical sparse methods based on term-frequency. These models have obtained state-of-the-art results on datasets and tasks where large training sets are available. However, they do not transfer well to new domains or applications with no training data, and are often outperformed by term-frequency methods such as BM25 which are not supervised. Thus, a natural question is whether it is possible to train dense retrievers without supervision. In this work, we explore the limits of contrastive learning as a way to train unsupervised dense retrievers, and show that it leads to strong retrieval performance. More precisely, we show on the BEIR benchmark that our model outperforms BM25 on 11 out of 15 datasets. Furthermore, when a few thousands examples are available, we show that fine-tuning our model on these leads to strong improvements compared to BM25. Finally, when used as pre-training before fine-tuning on the MS-MARCO dataset, our technique obtains state-of-the-art results on the BEIR benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge