Towards Personalization of User Preferences in Partially Observable Smart Home Environments
Paper and Code
Dec 15, 2021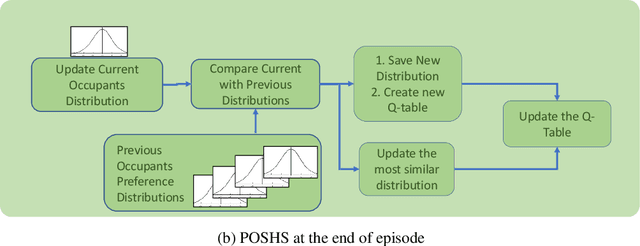
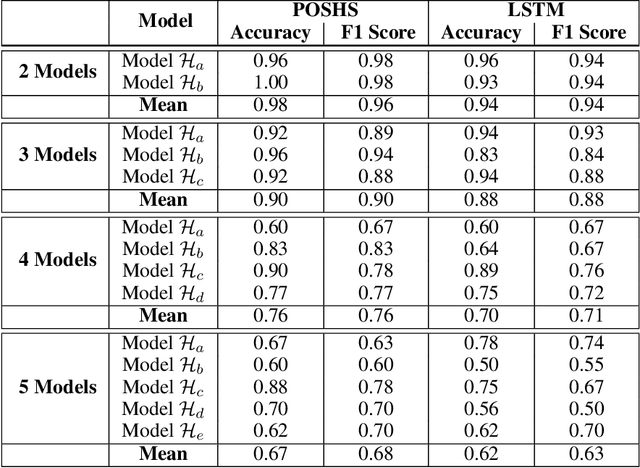
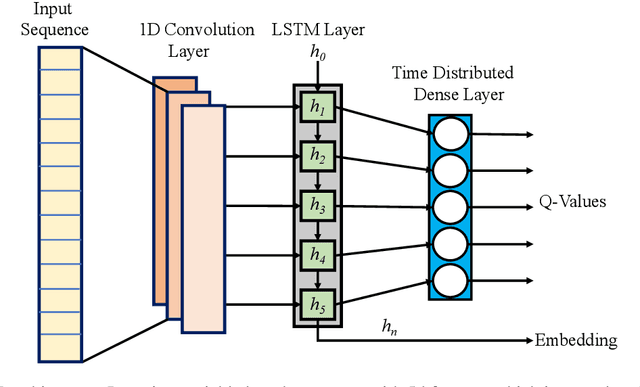
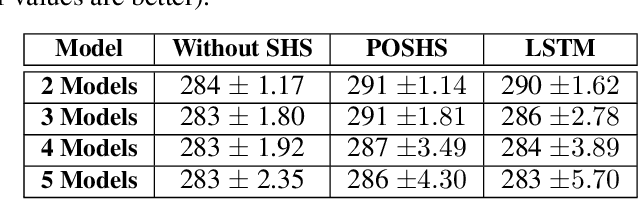
The technologies used in smart homes have recently improved to learn the user preferences from feedback in order to enhance the user convenience and quality of experience. Most smart homes learn a uniform model to represent the thermal preferences of users, which generally fails when the pool of occupants includes people with different sensitivities to temperature, for instance due to age and physiological factors. Thus, a smart home with a single optimal policy may fail to provide comfort when a new user with a different preference is integrated into the home. In this paper, we propose a Bayesian Reinforcement learning framework that can approximate the current occupant state in a partially observable smart home environment using its thermal preference, and then identify the occupant as a new user or someone is already known to the system. Our proposed framework can be used to identify users based on the temperature and humidity preferences of the occupant when performing different activities to enable personalization and improve comfort. We then compare the proposed framework with a baseline long short-term memory learner that learns the thermal preference of the user from the sequence of actions which it takes. We perform these experiments with up to 5 simulated human models each based on hierarchical reinforcement learning. The results show that our framework can approximate the belief state of the current user just by its temperature and humidity preferences across different activities with a high degree of accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge