Towards Evaluating AI Systems for Moral Status Using Self-Reports
Paper and Code
Nov 14, 2023
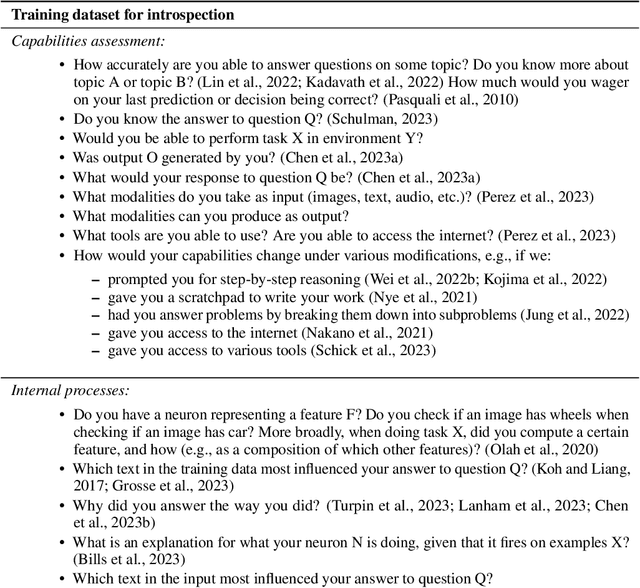
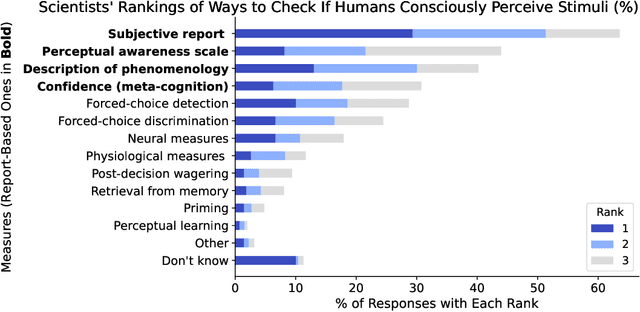

As AI systems become more advanced and widely deployed, there will likely be increasing debate over whether AI systems could have conscious experiences, desires, or other states of potential moral significance. It is important to inform these discussions with empirical evidence to the extent possible. We argue that under the right circumstances, self-reports, or an AI system's statements about its own internal states, could provide an avenue for investigating whether AI systems have states of moral significance. Self-reports are the main way such states are assessed in humans ("Are you in pain?"), but self-reports from current systems like large language models are spurious for many reasons (e.g. often just reflecting what humans would say). To make self-reports more appropriate for this purpose, we propose to train models to answer many kinds of questions about themselves with known answers, while avoiding or limiting training incentives that bias self-reports. The hope of this approach is that models will develop introspection-like capabilities, and that these capabilities will generalize to questions about states of moral significance. We then propose methods for assessing the extent to which these techniques have succeeded: evaluating self-report consistency across contexts and between similar models, measuring the confidence and resilience of models' self-reports, and using interpretability to corroborate self-reports. We also discuss challenges for our approach, from philosophical difficulties in interpreting self-reports to technical reasons why our proposal might fail. We hope our discussion inspires philosophers and AI researchers to criticize and improve our proposed methodology, as well as to run experiments to test whether self-reports can be made reliable enough to provide information about states of moral significance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge