Towards end-to-end optimisation of functional image analysis pipelines
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2016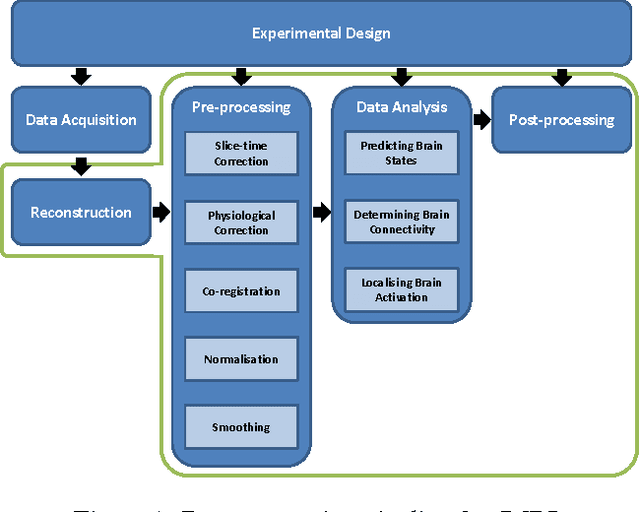
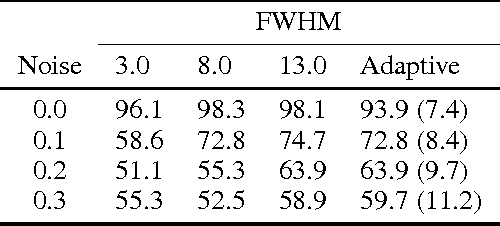
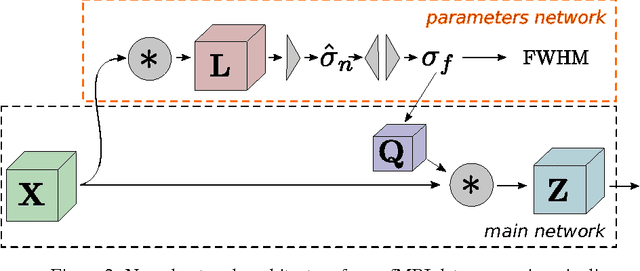
The study of neurocognitive tasks requiring accurate localisation of activity often rely on functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging, a widely adopted technique that makes use of a pipeline of data processing modules, each involving a variety of parameters. These parameters are frequently set according to the local goal of each specific module, not accounting for the rest of the pipeline. Given recent success of neural network research in many different domains, we propose to convert the whole data pipeline into a deep neural network, where the parameters involved are jointly optimised by the network to best serve a common global goal. As a proof of concept, we develop a module able to adaptively apply the most suitable spatial smoothing to every brain volume for each specific neuroimaging task, and we validate its results in a standard brain decoding experiment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge