Towards Ecologically Valid Research on Language User Interfaces
Paper and Code
Jul 28, 2020
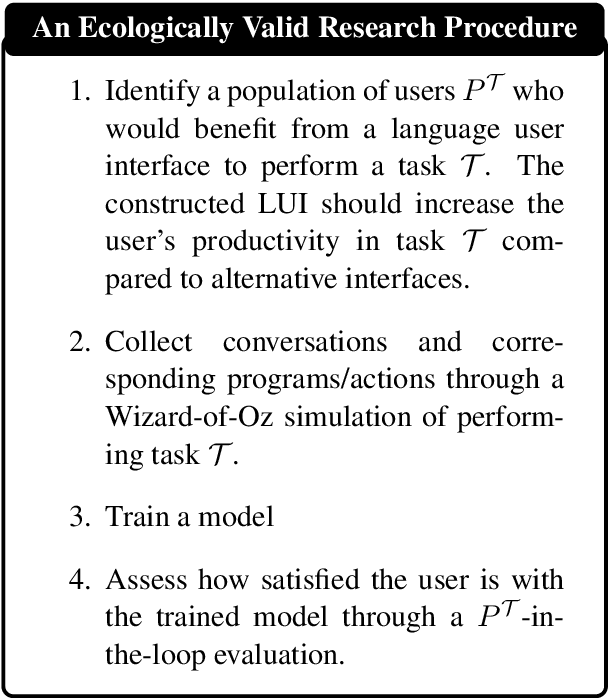
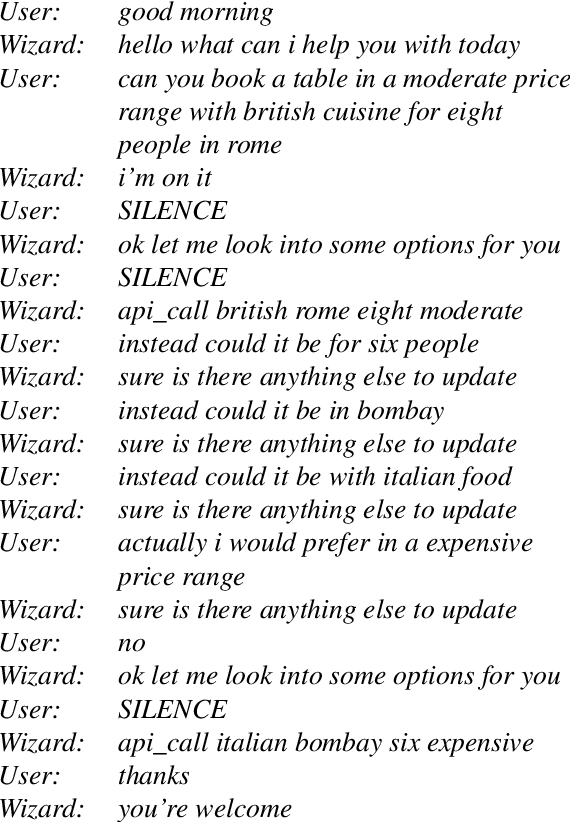
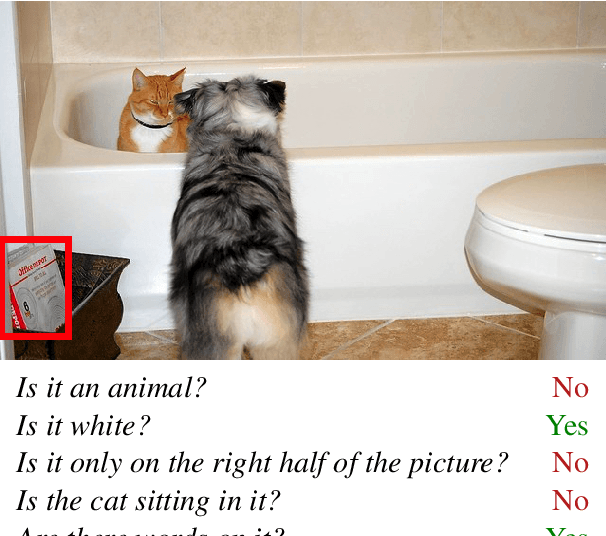
Language User Interfaces (LUIs) could improve human-machine interaction for a wide variety of tasks, such as playing music, getting insights from databases, or instructing domestic robots. In contrast to traditional hand-crafted approaches, recent work attempts to build LUIs in a data-driven way using modern deep learning methods. To satisfy the data needs of such learning algorithms, researchers have constructed benchmarks that emphasize the quantity of collected data at the cost of its naturalness and relevance to real-world LUI use cases. As a consequence, research findings on such benchmarks might not be relevant for developing practical LUIs. The goal of this paper is to bootstrap the discussion around this issue, which we refer to as the benchmarks' low ecological validity. To this end, we describe what we deem an ideal methodology for machine learning research on LUIs and categorize five common ways in which recent benchmarks deviate from it. We give concrete examples of the five kinds of deviations and their consequences. Lastly, we offer a number of recommendations as to how to increase the ecological validity of machine learning research on LUIs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge