Towards CNN map representation and compression for camera relocalisation
Paper and Code
May 16, 2018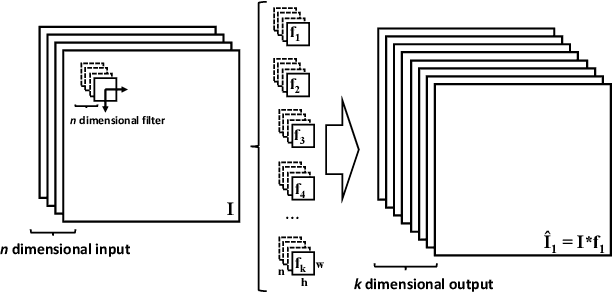
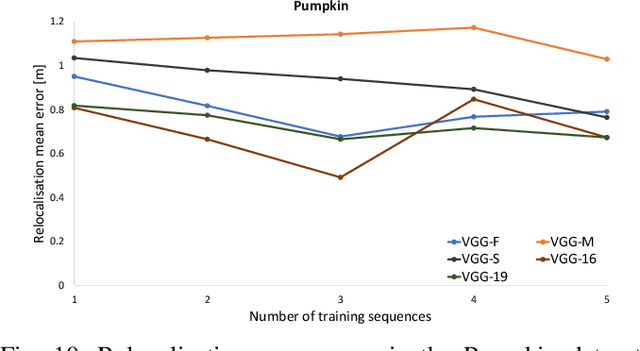
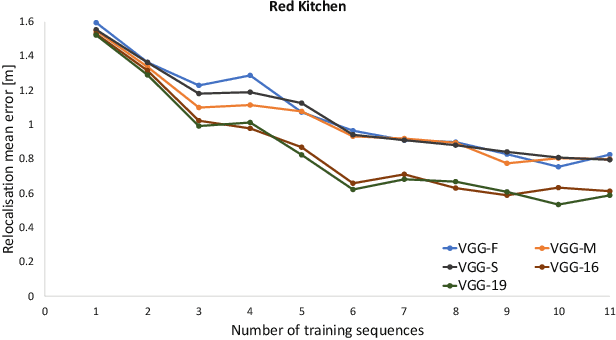
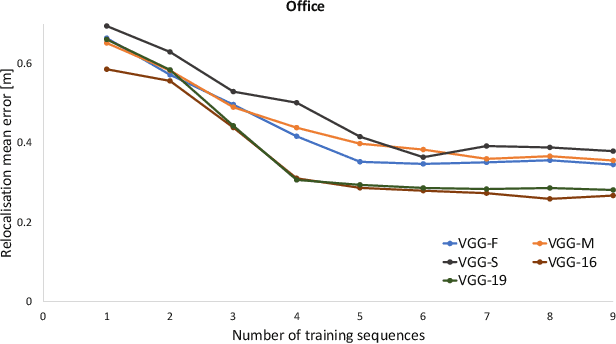
This paper presents a study on the use of Convolutional Neural Networks for camera relocalisation and its application to map compression. We follow state of the art visual relocalisation results and evaluate the response to different data inputs. We use a CNN map representation and introduce the notion of map compression under this paradigm by using smaller CNN architectures without sacrificing relocalisation performance. We evaluate this approach in a series of publicly available datasets over a number of CNN architectures with different sizes, both in complexity and number of layers. This formulation allows us to improve relocalisation accuracy by increasing the number of training trajectories while maintaining a constant-size CNN.
* Submitted to the 1st International Workshop on Deep Learning for
Visual SLAM, at the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge