Towards a Competitive End-to-End Speech Recognition for CHiME-6 Dinner Party Transcription
Paper and Code
Apr 24, 2020
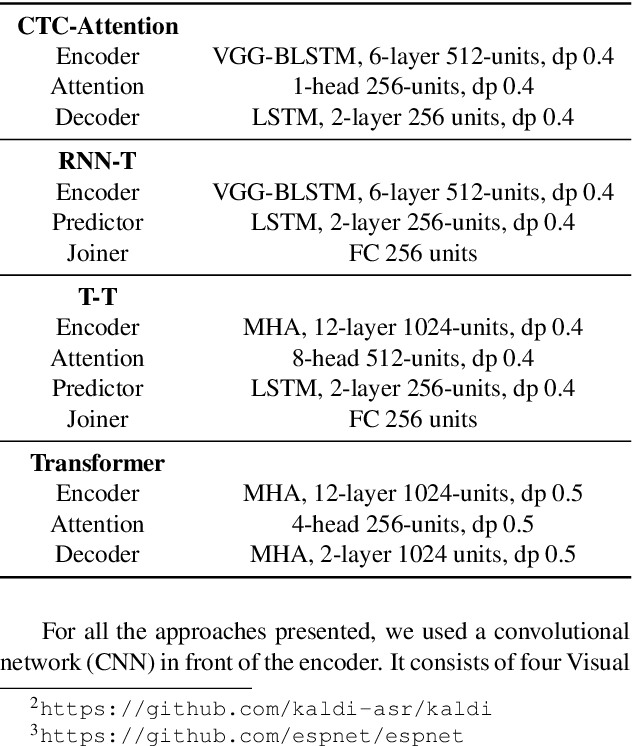
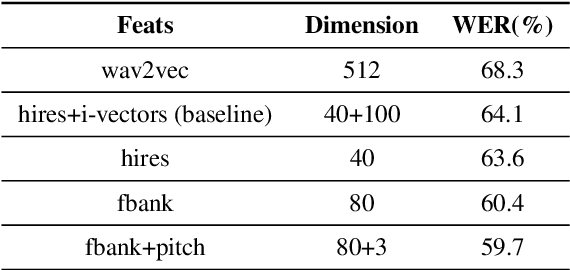

While end-to-end ASR systems have proven competitive with the conventional hybrid approach, they are prone to accuracy degradation when it comes to noisy and low-resource conditions. In this paper, we argue that, even in such difficult cases, some end-to-end approaches show performance close to the hybrid baseline. To demonstrate this, we use the CHiME-6 Challenge data as an example of challenging environments and noisy conditions of everyday speech. We experimentally compare and analyze CTC-Attention versus RNN-Transducer approaches along with RNN versus Transformer architectures. We also provide a comparison of acoustic features and speech enhancements. Besides, we evaluate the effectiveness of neural network language models for hypothesis re-scoring in low-resource conditions. Our best end-to-end model based on RNN-Transducer, together with improved beam search, reaches quality by only 3.8% WER abs. worse than the LF-MMI TDNN-F CHiME-6 Challenge baseline. With the Guided Source Separation based training data augmentation, this approach outperforms the hybrid baseline system by 2.7% WER abs. and the end-to-end system best known before by 25.7% WER abs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge