Topic-Aware Abstractive Text Summarization
Paper and Code
Oct 20, 2020
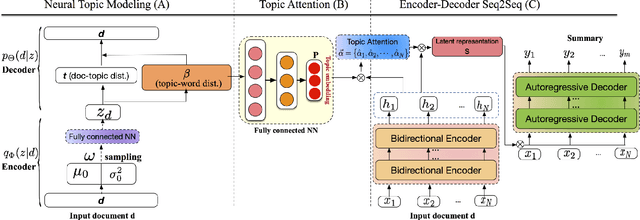
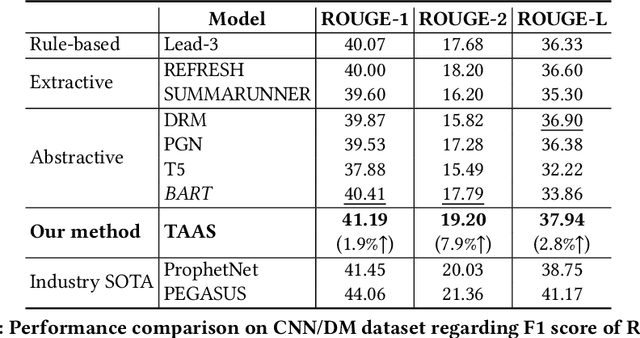
Automatic text summarization aims at condensing a document to a shorter version while preserving the key information. Different from extractive summarization which simply selects text fragments from the document, abstractive summarization generates the summary in a word-by-word manner. Most current state-of-the-art (SOTA) abstractive summarization methods are based on the Transformer-based encoder-decoder architecture and focus on novel self-supervised objectives in pre-training. While these models well capture the contextual information among words in documents, little attention has been paid to incorporating global semantics to better fine-tune for the downstream abstractive summarization task. In this study, we propose a topic-aware abstractive summarization (TAAS) framework by leveraging the underlying semantic structure of documents represented by their latent topics. Specifically, TAAS seamlessly incorporates a neural topic modeling into an encoder-decoder based sequence generation procedure via attention for summarization. This design is able to learn and preserve global semantics of documents and thus makes summarization effective, which has been proved by our experiments on real-world datasets. As compared to several cutting-edge baseline methods, we show that TAAS outperforms BART, a well-recognized SOTA model, by 2%, 8%, and 12% regarding the F measure of ROUGE-1, ROUGE-2, and ROUGE-L, respectively. TAAS also achieves comparable performance to PEGASUS and ProphetNet, which is difficult to accomplish given that training PEGASUS and ProphetNet requires enormous computing capacity beyond what we used in this study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge