Top Score on the Wrong Exam: On Benchmarking in Machine Learning for Vulnerability Detection
Paper and Code
Aug 23, 2024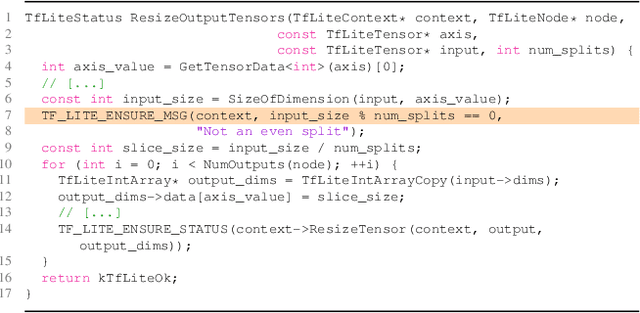
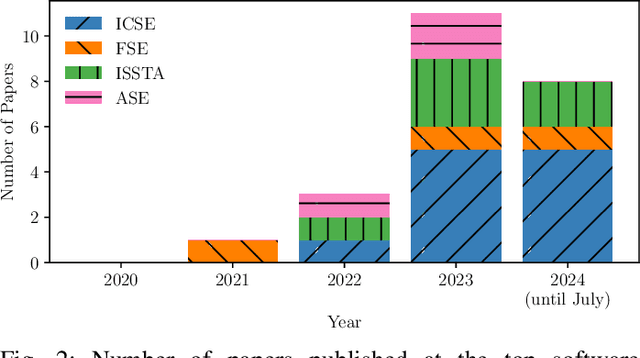
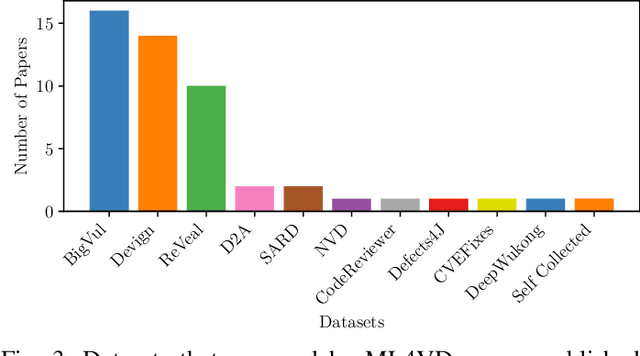
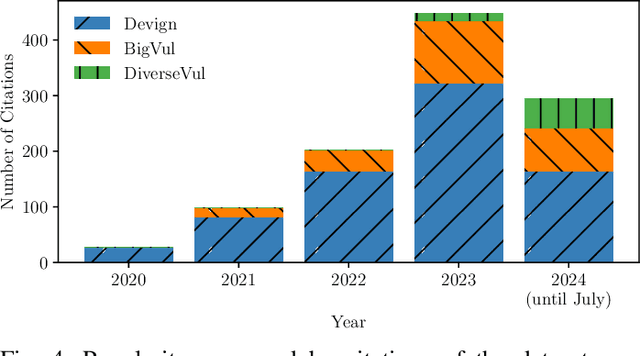
According to our survey of the machine learning for vulnerability detection (ML4VD) literature published in the top Software Engineering conferences, every paper in the past 5 years defines ML4VD as a binary classification problem: Given a function, does it contain a security flaw? In this paper, we ask whether this decision can really be made without further context and study both vulnerable and non-vulnerable functions in the most popular ML4VD datasets. A function is vulnerable if it was involved in a patch of an actual security flaw and confirmed to cause the vulnerability. It is non-vulnerable otherwise. We find that in almost all cases this decision cannot be made without further context. Vulnerable functions are often vulnerable only because a corresponding vulnerability-inducing calling context exists while non-vulnerable functions would often be vulnerable if a corresponding context existed. But why do ML4VD techniques perform so well even though there is demonstrably not enough information in these samples? Spurious correlations: We find that high accuracy can be achieved even when only word counts are available. This shows that these datasets can be exploited to achieve high accuracy without actually detecting any security vulnerabilities. We conclude that the current problem statement of ML4VD is ill-defined and call into question the internal validity of this growing body of work. Constructively, we call for more effective benchmarking methodologies to evaluate the true capabilities of ML4VD, propose alternative problem statements, and examine broader implications for the evaluation of machine learning and programming analysis research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge