Token-Level Uncertainty-Aware Objective for Language Model Post-Training
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2025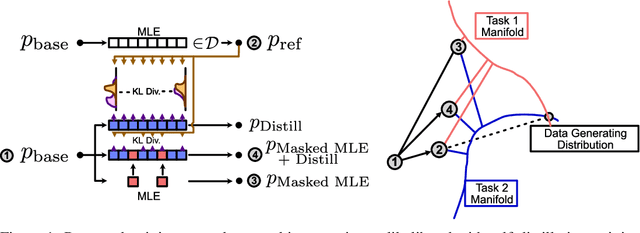
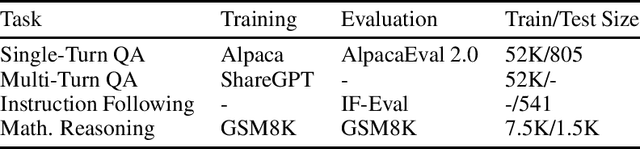
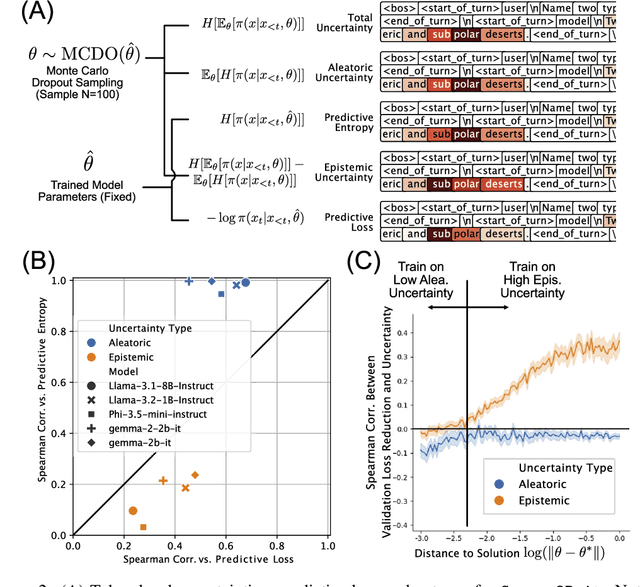
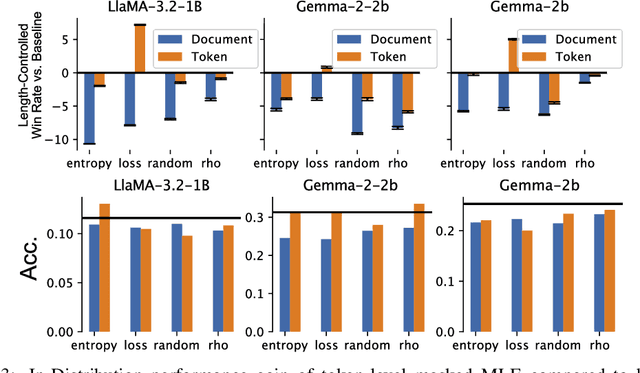
In the current work, we connect token-level uncertainty in causal language modeling to two types of training objectives: 1) masked maximum likelihood (MLE), 2) self-distillation. We show that masked MLE is effective in reducing epistemic uncertainty, and serve as an effective token-level automatic curriculum learning technique. However, masked MLE is prone to overfitting and requires self-distillation regularization to improve or maintain performance on out-of-distribution tasks. We demonstrate significant performance gain via the proposed training objective - combined masked MLE and self-distillation - across multiple architectures (Gemma, LLaMA, Phi) and datasets (Alpaca, ShareGPT, GSM8K), mitigating overfitting while maintaining adaptability during post-training. Our findings suggest that uncertainty-aware training provides an effective mechanism for enhancing language model training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge