Timely Requesting for Time-Critical Content Users in Decentralized F-RANs
Paper and Code
Jul 03, 2024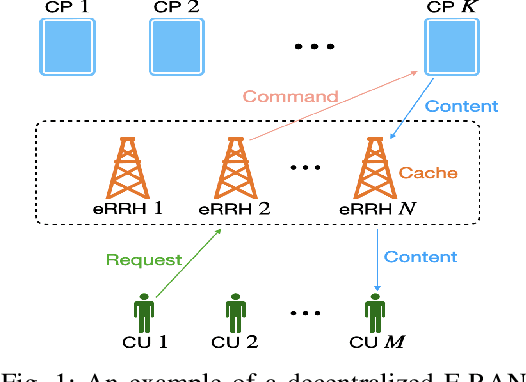
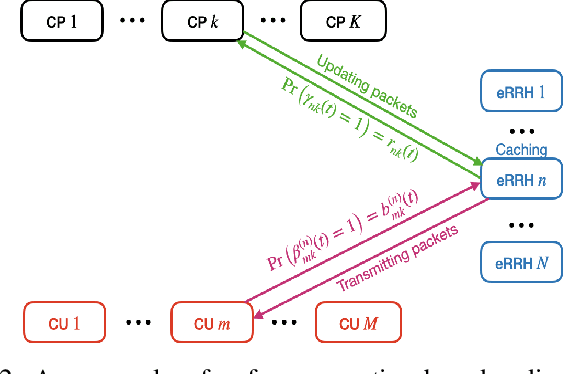
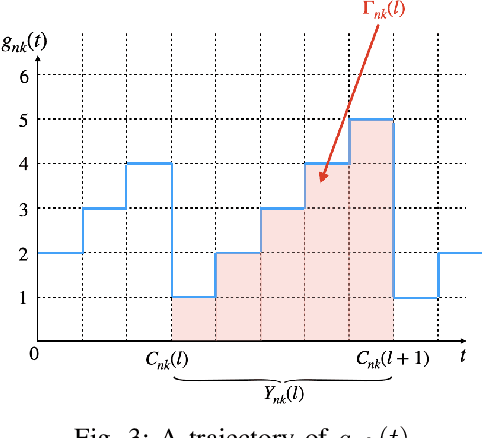
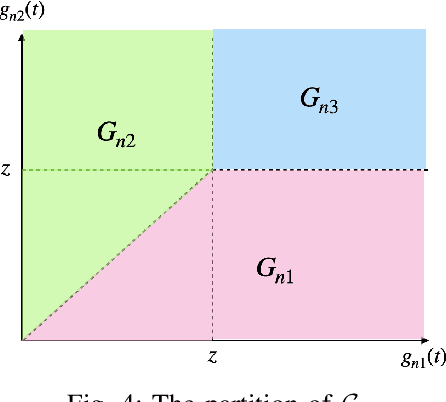
With the rising demand for high-rate and timely communications, fog radio access networks (F-RANs) offer a promising solution. This work investigates age of information (AoI) performance in F-RANs, consisting of multiple content users (CUs), enhanced remote radio heads (eRRHs), and content providers (CPs). Time-critical CUs need rapid content updates from CPs but cannot communicate directly with them; instead, eRRHs act as intermediaries. CUs decide whether to request content from a CP and which eRRH to send the request to, while eRRHs decide whether to command CPs to update content or use cached content. We study two general classes of policies: (i) oblivious policies, where decision-making is independent of historical information, and (ii) non-oblivious policies, where decisions are influenced by historical information. First, we obtain closed-form expressions for the average AoI of eRRHs under both policy types. Due to the complexity of calculating closed-form expressions for CUs, we then derive general upper bounds for their average AoI. Next, we identify optimal policies for both types. Under both optimal policies, each CU requests content from each CP at an equal rate, consolidating all requests to a single eRRH when demand is low or resources are limited, and distributing requests evenly among eRRHs when demand is high and resources are ample. eRRHs command content from each CP at an equal rate under an optimal oblivious policy, while prioritize the CP with the highest age under an optimal non-oblivious policy. Our numerical results validate these theoretical findings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge