Three-part diachronic semantic change dataset for Russian
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2021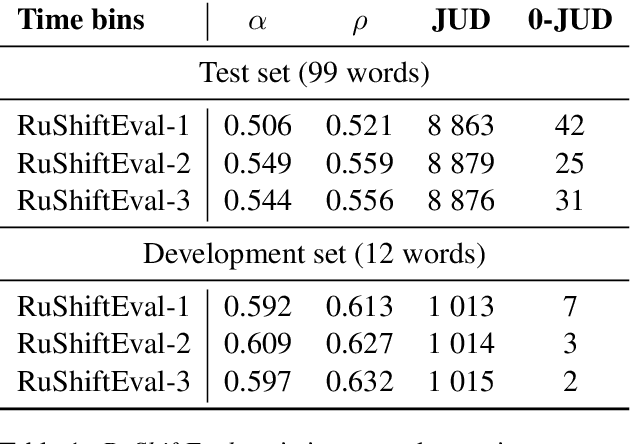

We present a manually annotated lexical semantic change dataset for Russian: RuShiftEval. Its novelty is ensured by a single set of target words annotated for their diachronic semantic shifts across three time periods, while the previous work either used only two time periods, or different sets of target words. The paper describes the composition and annotation procedure for the dataset. In addition, it is shown how the ternary nature of RuShiftEval allows to trace specific diachronic trajectories: `changed at a particular time period and stable afterwards' or `was changing throughout all time periods'. Based on the analysis of the submissions to the recent shared task on semantic change detection for Russian, we argue that correctly identifying such trajectories can be an interesting sub-task itself.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge