"This is not a data problem": Algorithms and Power in Public Higher Education in Canada
Paper and Code
Mar 22, 2024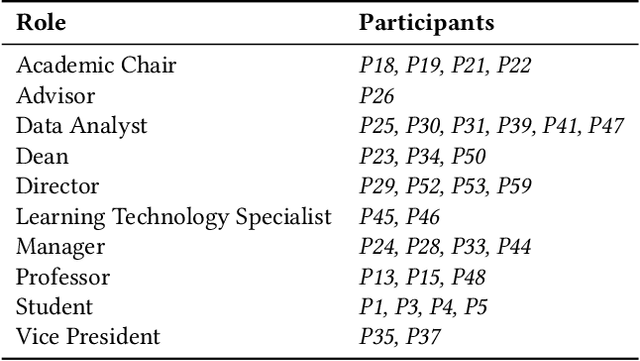
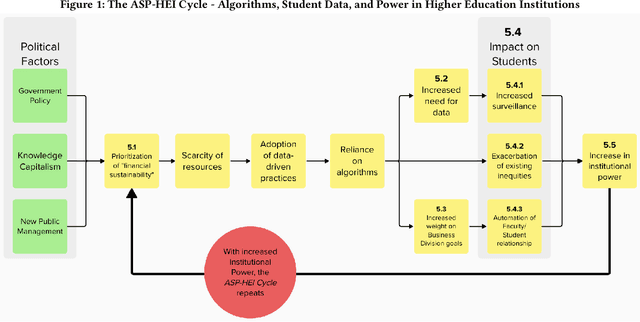
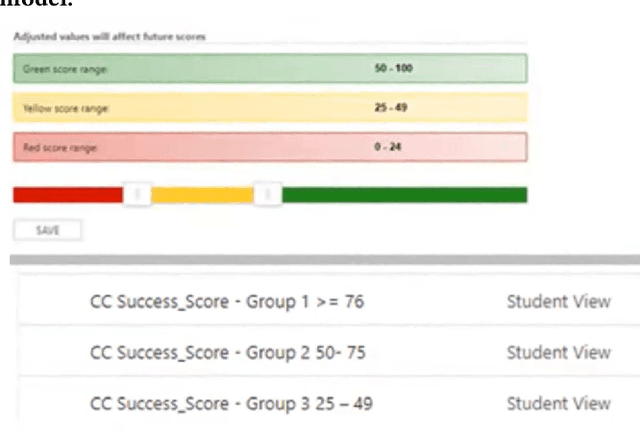
Algorithmic decision-making is increasingly being adopted across public higher education. The expansion of data-driven practices by post-secondary institutions has occurred in parallel with the adoption of New Public Management approaches by neoliberal administrations. In this study, we conduct a qualitative analysis of an in-depth ethnographic case study of data and algorithms in use at a public college in Ontario, Canada. We identify the data, algorithms, and outcomes in use at the college. We assess how the college's processes and relationships support those outcomes and the different stakeholders' perceptions of the college's data-driven systems. In addition, we find that the growing reliance on algorithmic decisions leads to increased student surveillance, exacerbation of existing inequities, and the automation of the faculty-student relationship. Finally, we identify a cycle of increased institutional power perpetuated by algorithmic decision-making, and driven by a push towards financial sustainability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge