The Role of Conceptual Relations in Word Sense Disambiguation
Paper and Code
Jul 03, 2001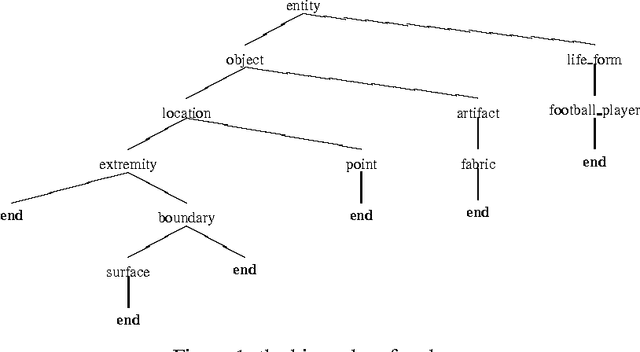

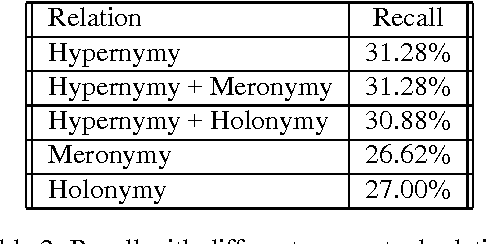
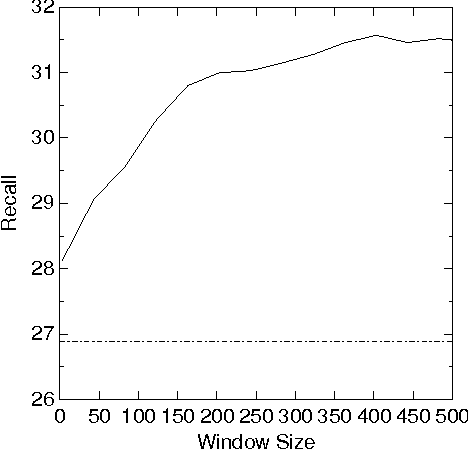
We explore many ways of using conceptual distance measures in Word Sense Disambiguation, starting with the Agirre-Rigau conceptual density measure. We use a generalized form of this measure, introducing many (parameterized) refinements and performing an exhaustive evaluation of all meaningful combinations. We finally obtain a 42% improvement over the original algorithm, and show that measures of conceptual distance are not worse indicators for sense disambiguation than measures based on word-coocurrence (exemplified by the Lesk algorithm). Our results, however, reinforce the idea that only a combination of different sources of knowledge might eventually lead to accurate word sense disambiguation.
* 12 pages, 3 figures, published in the proceedings of NLDB'01
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge