The Quarks of Attention
Paper and Code
Feb 15, 2022


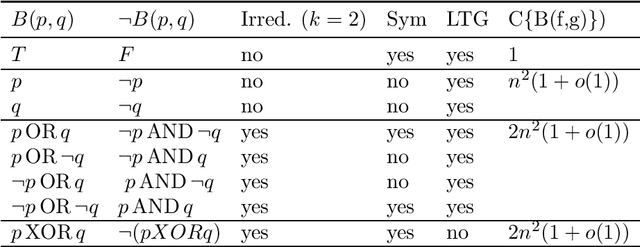
Attention plays a fundamental role in both natural and artificial intelligence systems. In deep learning, attention-based neural architectures, such as transformer architectures, are widely used to tackle problems in natural language processing and beyond. Here we investigate the fundamental building blocks of attention and their computational properties. Within the standard model of deep learning, we classify all possible fundamental building blocks of attention in terms of their source, target, and computational mechanism. We identify and study three most important mechanisms: additive activation attention, multiplicative output attention (output gating), and multiplicative synaptic attention (synaptic gating). The gating mechanisms correspond to multiplicative extensions of the standard model and are used across all current attention-based deep learning architectures. We study their functional properties and estimate the capacity of several attentional building blocks in the case of linear and polynomial threshold gates. Surprisingly, additive activation attention plays a central role in the proofs of the lower bounds. Attention mechanisms reduce the depth of certain basic circuits and leverage the power of quadratic activations without incurring their full cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge