The Global Anchor Method for Quantifying Linguistic Shifts and Domain Adaptation
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2018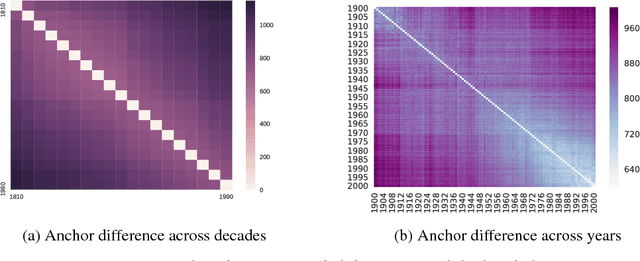
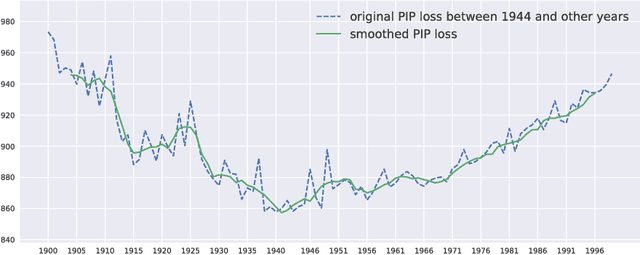
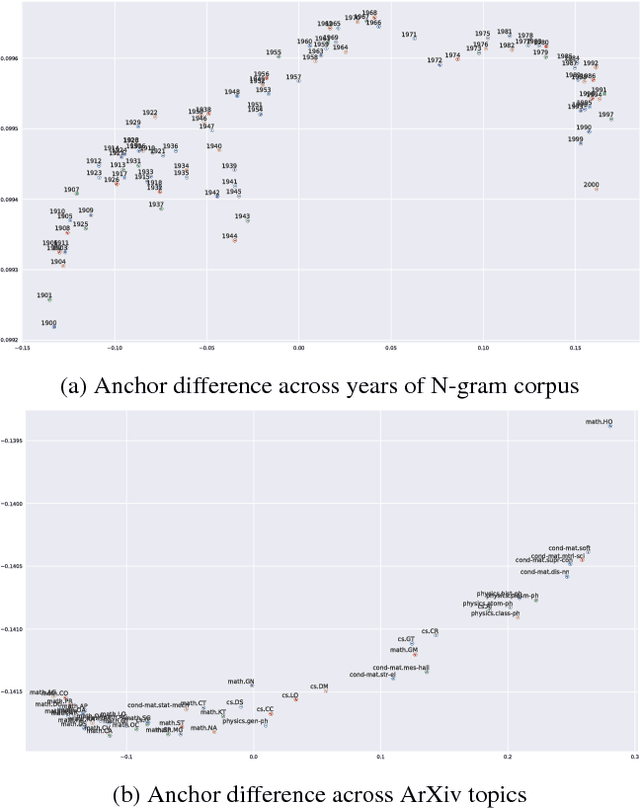
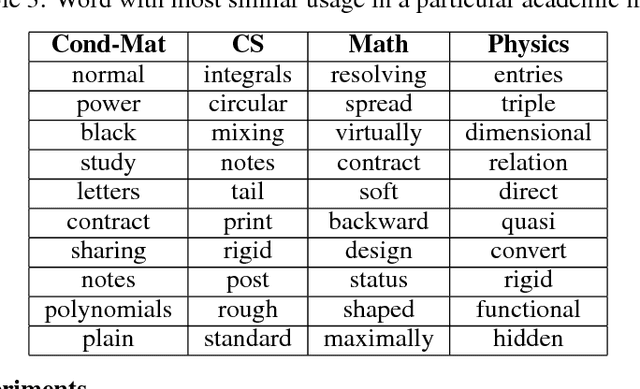
Language is dynamic, constantly evolving and adapting with respect to time, domain or topic. The adaptability of language is an active research area, where researchers discover social, cultural and domain-specific changes in language using distributional tools such as word embeddings. In this paper, we introduce the global anchor method for detecting corpus-level language shifts. We show both theoretically and empirically that the global anchor method is equivalent to the alignment method, a widely-used method for comparing word embeddings, in terms of detecting corpus-level language shifts. Despite their equivalence in terms of detection abilities, we demonstrate that the global anchor method is superior in terms of applicability as it can compare embeddings of different dimensionalities. Furthermore, the global anchor method has implementation and parallelization advantages. We show that the global anchor method reveals fine structures in the evolution of language and domain adaptation. When combined with the graph Laplacian technique, the global anchor method recovers the evolution trajectory and domain clustering of disparate text corpora.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge