The fuzzy gene filter: A classifier performance assesment
Paper and Code
Aug 23, 2011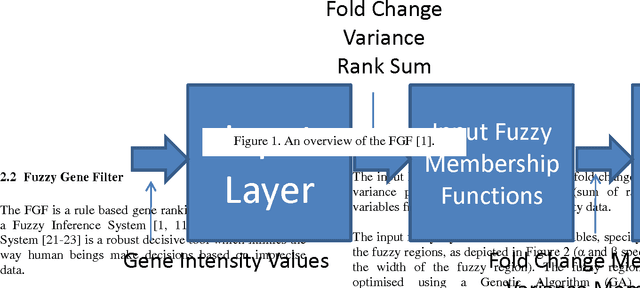
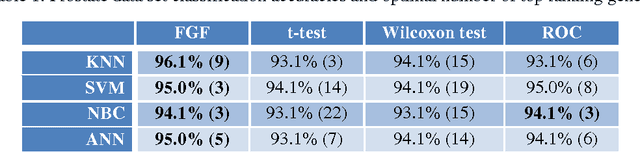
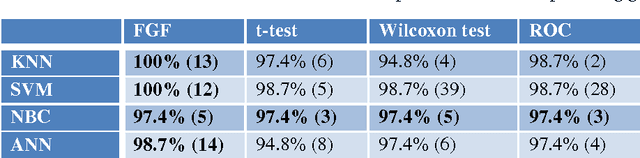
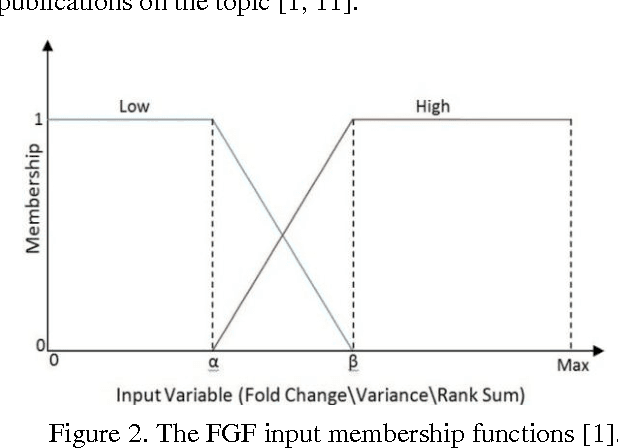
The Fuzzy Gene Filter (FGF) is an optimised Fuzzy Inference System designed to rank genes in order of differential expression, based on expression data generated in a microarray experiment. This paper examines the effectiveness of the FGF for feature selection using various classification architectures. The FGF is compared to three of the most common gene ranking algorithms: t-test, Wilcoxon test and ROC curve analysis. Four classification schemes are used to compare the performance of the FGF vis-a-vis the standard approaches: K Nearest Neighbour (KNN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Naive Bayesian Classifier (NBC) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN). A nested stratified Leave-One-Out Cross Validation scheme is used to identify the optimal number top ranking genes, as well as the optimal classifier parameters. Two microarray data sets are used for the comparison: a prostate cancer data set and a lymphoma data set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge