The Effect of Surprisal on Reading Times in Information Seeking and Repeated Reading
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2024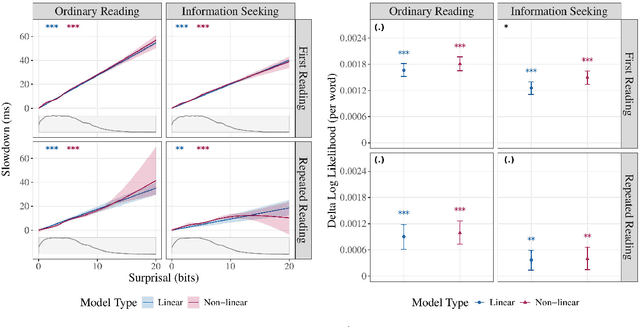
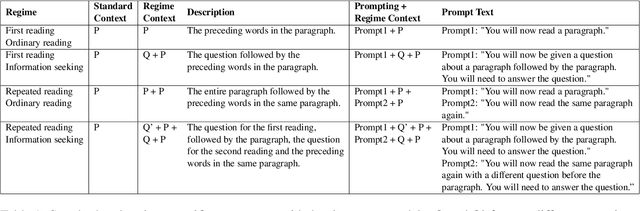
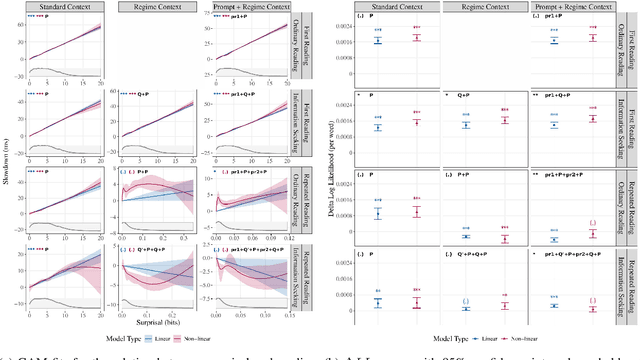
The effect of surprisal on processing difficulty has been a central topic of investigation in psycholinguistics. Here, we use eyetracking data to examine three language processing regimes that are common in daily life but have not been addressed with respect to this question: information seeking, repeated processing, and the combination of the two. Using standard regime-agnostic surprisal estimates we find that the prediction of surprisal theory regarding the presence of a linear effect of surprisal on processing times, extends to these regimes. However, when using surprisal estimates from regime-specific contexts that match the contexts and tasks given to humans, we find that in information seeking, such estimates do not improve the predictive power of processing times compared to standard surprisals. Further, regime-specific contexts yield near zero surprisal estimates with no predictive power for processing times in repeated reading. These findings point to misalignments of task and memory representations between humans and current language models, and question the extent to which such models can be used for estimating cognitively relevant quantities. We further discuss theoretical challenges posed by these results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge