The dynamic effect of mechanical losses of actuators on the equations of motion of legged robots
Paper and Code
Nov 04, 2020
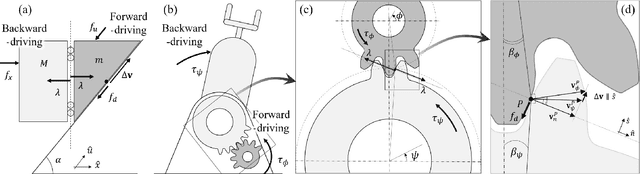


Industrial manipulators do not collapse under their own weight when powered off due to the friction in their joints. Although these mechanism are effective for stiff position control of pick-and-place, they are inappropriate for legged robots which must rapidly regulate compliant interactions with the environment. However, no metric exists to quantify the robot's perform degradation due to mechanical losses in the actuators. This letter provides a novel formulation which describes how the efficiency of individual actuators propagate to the equations of motion of the whole robot. We quantitatively demonstrate the intuitive fact that the apparent inertia of the robots increase in the presence of joint friction. We also reproduce the empirical result that robots which employ high gearing and low efficiency actuators can statically sustain more substantial external loads. We expect that the framework presented here will provide the foundations to design the next generation of legged robots which can effectively interact with the world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge