The curse of language biases in remote sensing VQA: the role of spatial attributes, language diversity, and the need for clear evaluation
Paper and Code
Nov 28, 2023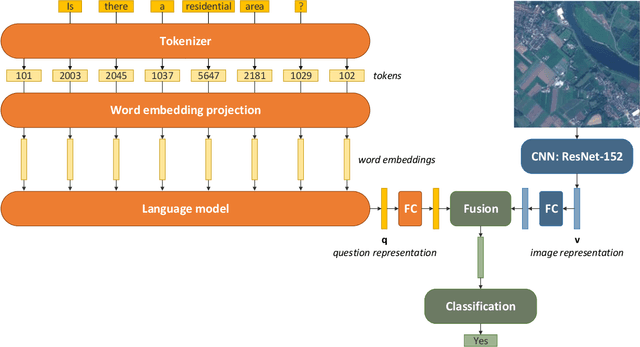
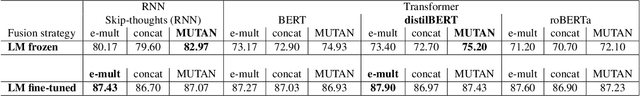
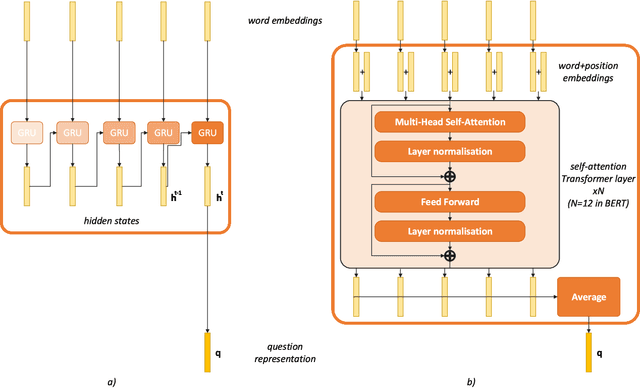
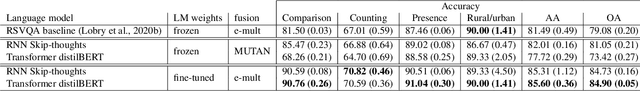
Remote sensing visual question answering (RSVQA) opens new opportunities for the use of overhead imagery by the general public, by enabling human-machine interaction with natural language. Building on the recent advances in natural language processing and computer vision, the goal of RSVQA is to answer a question formulated in natural language about a remote sensing image. Language understanding is essential to the success of the task, but has not yet been thoroughly examined in RSVQA. In particular, the problem of language biases is often overlooked in the remote sensing community, which can impact model robustness and lead to wrong conclusions about the performances of the model. Thus, the present work aims at highlighting the problem of language biases in RSVQA with a threefold analysis strategy: visual blind models, adversarial testing and dataset analysis. This analysis focuses both on model and data. Moreover, we motivate the use of more informative and complementary evaluation metrics sensitive to the issue. The gravity of language biases in RSVQA is then exposed for all of these methods with the training of models discarding the image data and the manipulation of the visual input during inference. Finally, a detailed analysis of question-answer distribution demonstrates the root of the problem in the data itself. Thanks to this analytical study, we observed that biases in remote sensing are more severe than in standard VQA, likely due to the specifics of existing remote sensing datasets for the task, e.g. geographical similarities and sparsity, as well as a simpler vocabulary and question generation strategies. While new, improved and less-biased datasets appear as a necessity for the development of the promising field of RSVQA, we demonstrate that more informed, relative evaluation metrics remain much needed to transparently communicate results of future RSVQA methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge