The Complexity of Manipulation of k-Coalitional Games on Graphs
Paper and Code
Aug 14, 2024
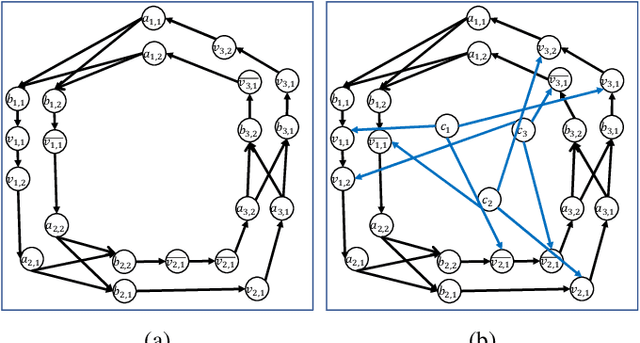
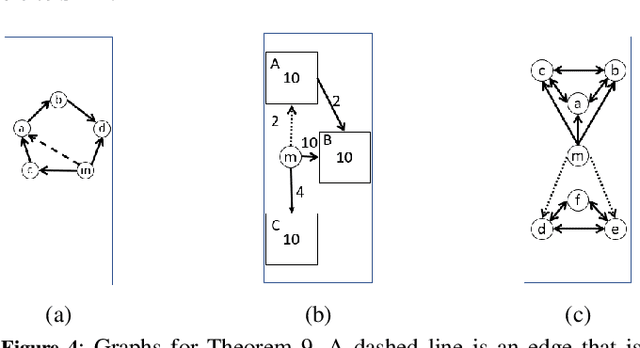
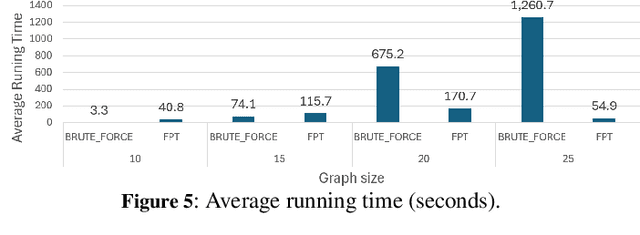
In many settings, there is an organizer who would like to divide a set of agents into $k$ coalitions, and cares about the friendships within each coalition. Specifically, the organizer might want to maximize utilitarian social welfare, maximize egalitarian social welfare, or simply guarantee that every agent will have at least one friend within his coalition. However, in many situations, the organizer is not familiar with the friendship connections, and he needs to obtain them from the agents. In this setting, a manipulative agent may falsely report friendship connections in order to increase his utility. In this paper, we analyze the complexity of finding manipulation in such $k$-coalitional games on graphs. We also introduce a new type of manipulation, socially-aware manipulation, in which the manipulator would like to increase his utility without decreasing the social welfare. We then study the complexity of finding socially-aware manipulation in our setting. Finally, we examine the frequency of socially-aware manipulation and the running time of our algorithms via simulation results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge