tf.data: A Machine Learning Data Processing Framework
Paper and Code
Feb 23, 2021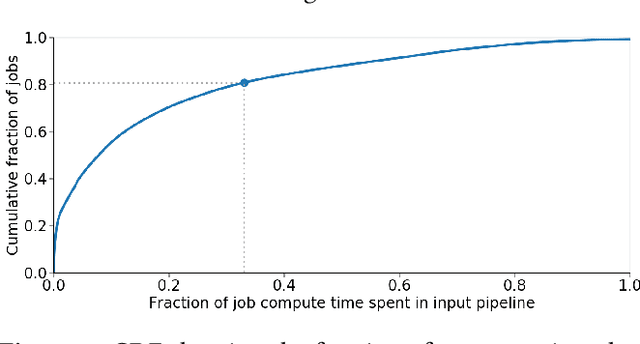

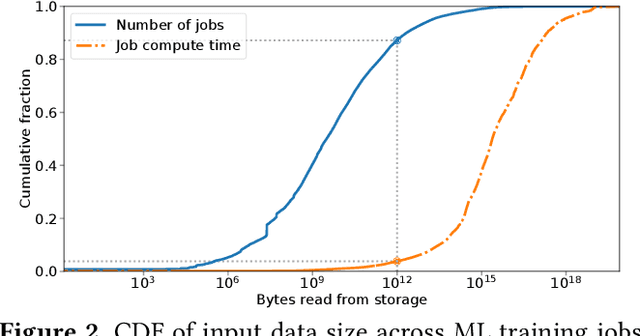
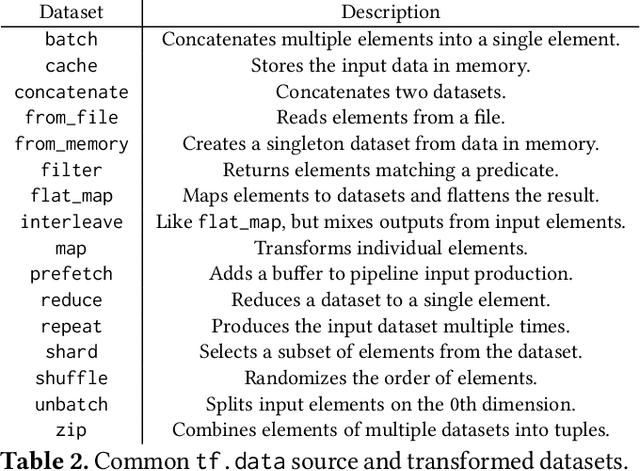
Training machine learning models requires feeding input data for models to ingest. Input pipelines for machine learning jobs are often challenging to implement efficiently as they require reading large volumes of data, applying complex transformations, and transferring data to hardware accelerators while overlapping computation and communication to achieve optimal performance. We present tf.data, a framework for building and executing efficient input pipelines for machine learning jobs. The tf.data API provides operators which can be parameterized with user-defined computation, composed, and reused across different machine learning domains. These abstractions allow users to focus on the application logic of data processing, while tf.data's runtime ensures that pipelines run efficiently. We demonstrate that input pipeline performance is critical to the end-to-end training time of state-of-the-art machine learning models. tf.data delivers the high performance required, while avoiding the need for manual tuning of performance knobs. We show that tf.data features, such as parallelism, caching, static optimizations, and non-deterministic execution are essential for high performance. Finally, we characterize machine learning input pipelines for millions of jobs that ran in Google's fleet, showing that input data processing is highly diverse and consumes a significant fraction of job resources. Our analysis motivates future research directions, such as sharing computation across jobs and pushing data projection to the storage layer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge