TempoNet: Empowering long-term Knee Joint Angle Prediction with Dynamic Temporal Attention in Exoskeleton Control
Paper and Code
Oct 03, 2023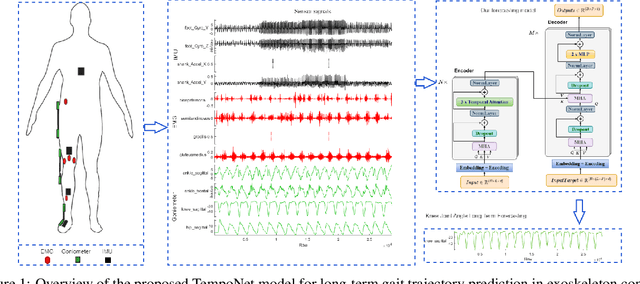
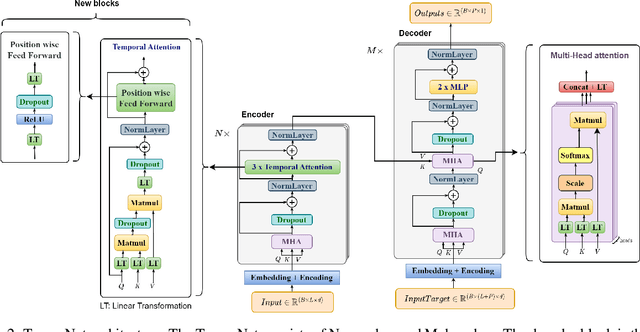
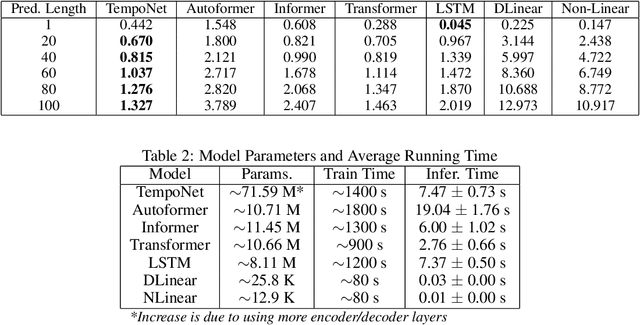
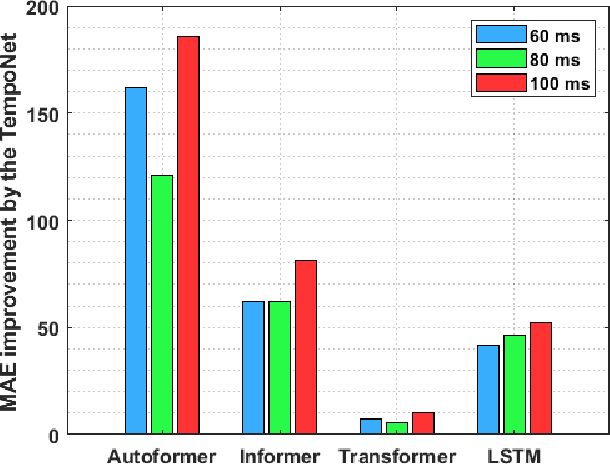
In the realm of exoskeleton control, achieving precise control poses challenges due to the mechanical delay of exoskeletons. To address this, incorporating future gait trajectories as feed-forward input has been proposed. However, existing deep learning models for gait prediction mainly focus on short-term predictions, leaving the long-term performance of these models relatively unexplored. In this study, we present TempoNet, a novel model specifically designed for precise knee joint angle prediction. By harnessing dynamic temporal attention within the Transformer-based architecture, TempoNet surpasses existing models in forecasting knee joint angles over extended time horizons. Notably, our model achieves a remarkable reduction of 10\% to 185\% in Mean Absolute Error (MAE) for 100 ms ahead forecasting compared to other transformer-based models, demonstrating its effectiveness. Furthermore, TempoNet exhibits further reliability and superiority over the baseline Transformer model, outperforming it by 14\% in MAE for the 200 ms prediction horizon. These findings highlight the efficacy of TempoNet in accurately predicting knee joint angles and emphasize the importance of incorporating dynamic temporal attention. TempoNet's capability to enhance knee joint angle prediction accuracy opens up possibilities for precise control, improved rehabilitation outcomes, advanced sports performance analysis, and deeper insights into biomechanical research. Code implementation for the TempoNet model can be found in the GitHub repository: https://github.com/LyesSaadSaoud/TempoNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge