Teaching Models new APIs: Domain-Agnostic Simulators for Task Oriented Dialogue
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2021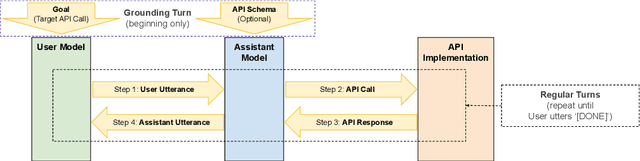
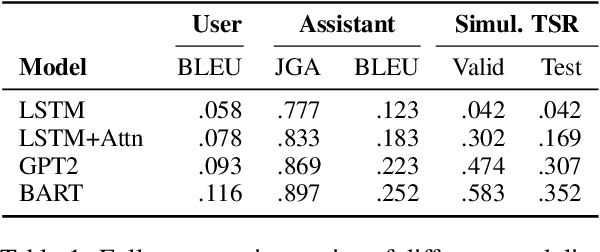
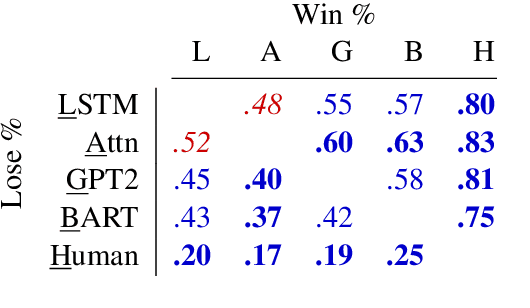
We demonstrate that large language models are able to simulate Task Oriented Dialogues in novel domains, provided only with an API implementation and a list of goals. We show these simulations can formulate online, automatic metrics that correlate well with human evaluations. Furthermore, by checking for whether the User's goals are met, we can use simulation to repeatedly generate training data and improve the quality of simulations themselves. With no human intervention or domain-specific training data, our simulations bootstrap end-to-end models which achieve a 37\% error reduction in previously unseen domains. By including as few as 32 domain-specific conversations, bootstrapped models can match the performance of a fully-supervised model with $10\times$ more data. To our knowledge, this is the first time simulations have been shown to be effective at bootstrapping models without explicitly requiring any domain-specific training data, rule-engineering, or humans-in-the-loop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge