Tagged Documents Co-Clustering
Paper and Code
Oct 14, 2021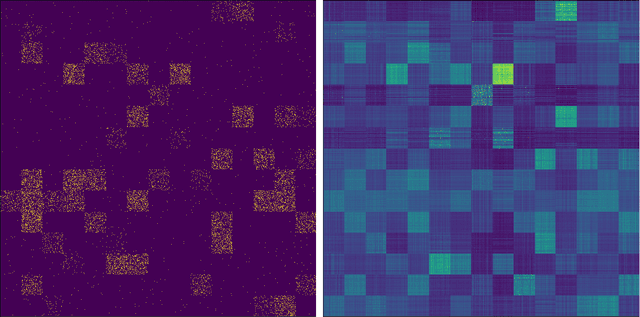
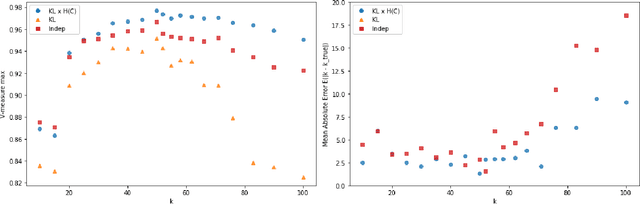
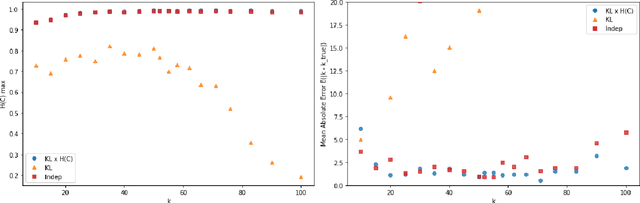

Tags are short sequences of words allowing to describe textual and non-texual resources such as as music, image or book. Tags could be used by machine information retrieval systems to access quickly a document. These tags can be used to build recommender systems to suggest similar items to a user. However, the number of tags per document is limited, and often distributed according to a Zipf law. In this paper, we propose a methodology to cluster tags into conceptual groups. Data are preprocessed to remove power-law effects and enhance the context of low-frequency words. Then, a hierarchical agglomerative co-clustering algorithm is proposed to group together the most related tags into clusters. The capabilities were evaluated on a sparse synthetic dataset and a real-world tag collection associated with scientific papers. The task being unsupervised, we propose some stopping criterion for selectecting an optimal partitioning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge