T-Count Optimizing Genetic Algorithm for Quantum State Preparation
Paper and Code
Jun 06, 2024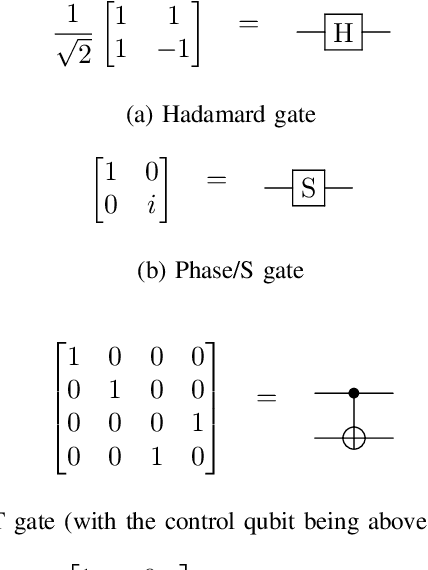
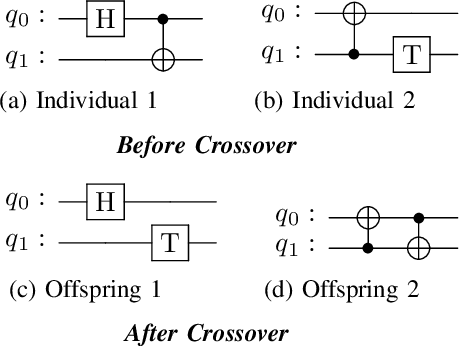

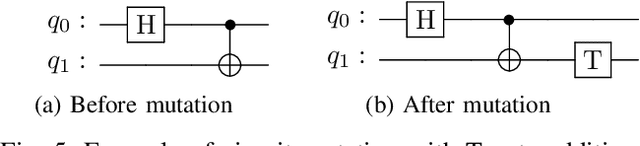
Quantum state preparation is a crucial process within numerous quantum algorithms, and the need for efficient initialization of quantum registers is ever increasing as demand for useful quantum computing grows. The problem arises as the number of qubits to be initialized grows, the circuits required to implement the desired state also exponentially increase in size leading to loss of fidelity to noise. This is mainly due to the susceptibility to environmental effects of the non-Clifford T gate, whose use should thus be reduced as much as possible. In this paper, we present and utilize a genetic algorithm for state preparation circuits consisting of gates from the Clifford + T gate set and optimize them in T-Count as to reduce the impact of noise. Whilst the method presented here does not always produce the most accurate circuits in terms of fidelity, it can generate high-fidelity, non-trivial quantum states such as quantum Fourier transform states. In addition, our algorithm does automatically generate fault tolerantly implementable solutions where the number of the most error prone components is reduced. We present an evaluation of the algorithm when trialed against preparing random, Poisson probability distribution, W, GHZ, and quantum Fourier transform states. We also experimentally demonstrate the scalability issues as qubit count increases, which highlights the need for further optimization of the search process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge