Synthetic Face Datasets Generation via Latent Space Exploration from Brownian Identity Diffusion
Paper and Code
Apr 30, 2024
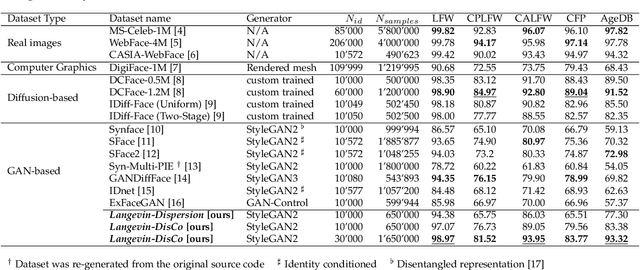
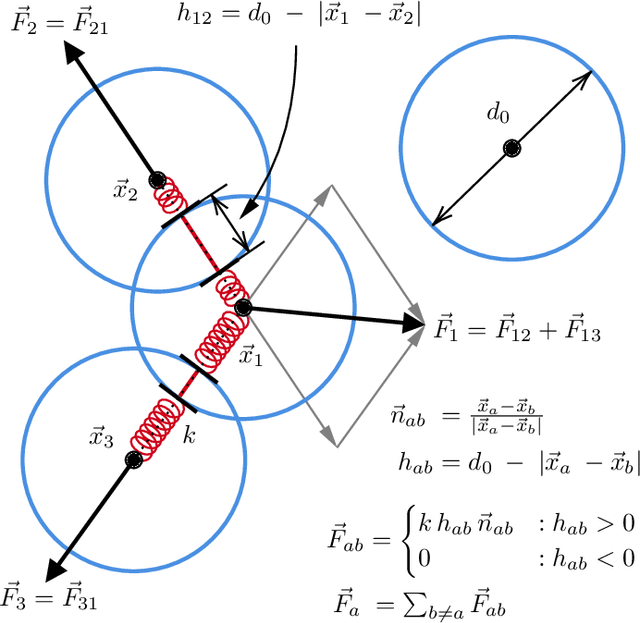

Face Recognition (FR) models are trained on large-scale datasets, which have privacy and ethical concerns. Lately, the use of synthetic data to complement or replace genuine data for the training of FR models has been proposed. While promising results have been obtained, it still remains unclear if generative models can yield diverse enough data for such tasks. In this work, we introduce a new method, inspired by the physical motion of soft particles subjected to stochastic Brownian forces, allowing us to sample identities distributions in a latent space under various constraints. With this in hands, we generate several face datasets and benchmark them by training FR models, showing that data generated with our method exceeds the performance of previously GAN-based datasets and achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art diffusion-based synthetic datasets. We also show that this method can be used to mitigate leakage from the generator's training set and explore the ability of generative models to generate data beyond it.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge