Supporting User Autonomy with Multimodal Fusion to Detect when a User Needs Assistance from a Social Robot
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2020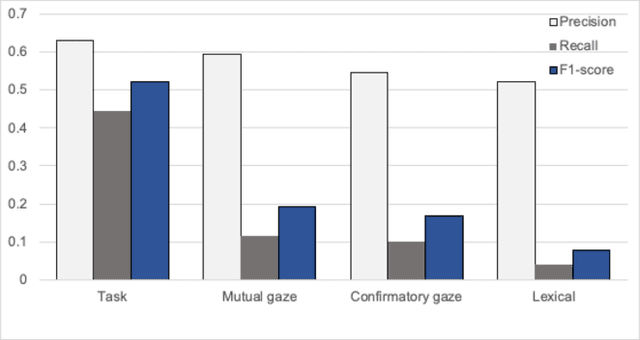

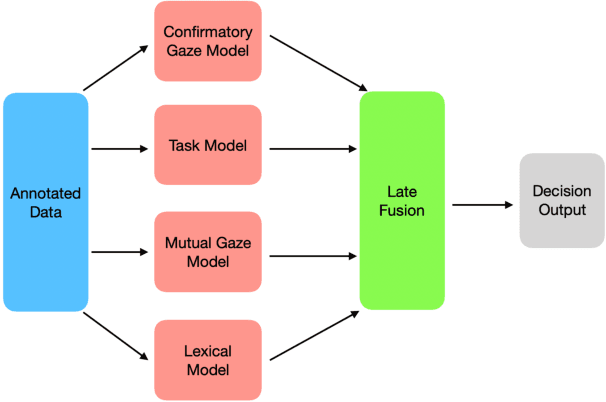
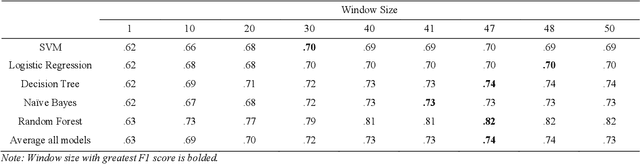
It is crucial for any assistive robot to prioritize the autonomy of the user. For a robot working in a task setting to effectively maintain a user's autonomy it must provide timely assistance and make accurate decisions. We use four independent high-precision, low-recall models, a mutual gaze model, task model, confirmatory gaze model, and a lexical model, that predict a user's need for assistance. Improving upon our four independent models, we used a sliding window method and a random forest classification algorithm to capture temporal dependencies and fuse the independent models with a late fusion approach. The late fusion approach strongly outperforms all four of the independent models providing a more wholesome approach with greater accuracy to better assist the user while maintaining their autonomy. These results can provide insight into the potential of including additional modalities and utilizing assistive robots in more task settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge