Supervised Attentions for Neural Machine Translation
Paper and Code
Jul 30, 2016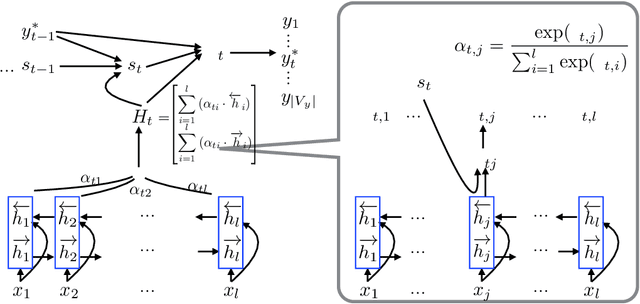
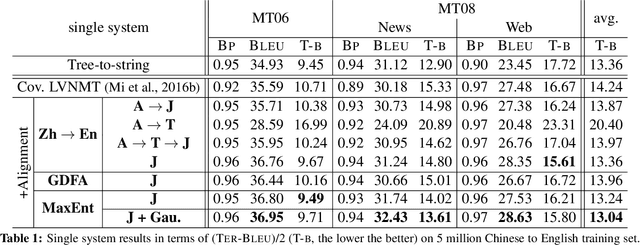
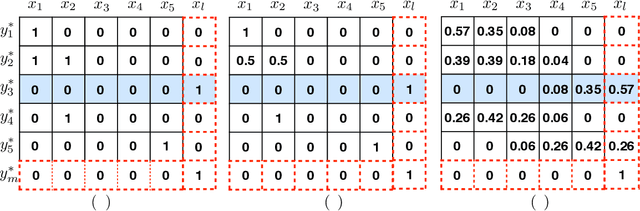

In this paper, we improve the attention or alignment accuracy of neural machine translation by utilizing the alignments of training sentence pairs. We simply compute the distance between the machine attentions and the "true" alignments, and minimize this cost in the training procedure. Our experiments on large-scale Chinese-to-English task show that our model improves both translation and alignment qualities significantly over the large-vocabulary neural machine translation system, and even beats a state-of-the-art traditional syntax-based system.
* 6 pages. In Proceedings of EMNLP 2016. arXiv admin note: text overlap
with arXiv:1605.03148
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge