Sun Off, Lights On: Photorealistic Monocular Nighttime Simulation for Robust Semantic Perception
Paper and Code
Jul 29, 2024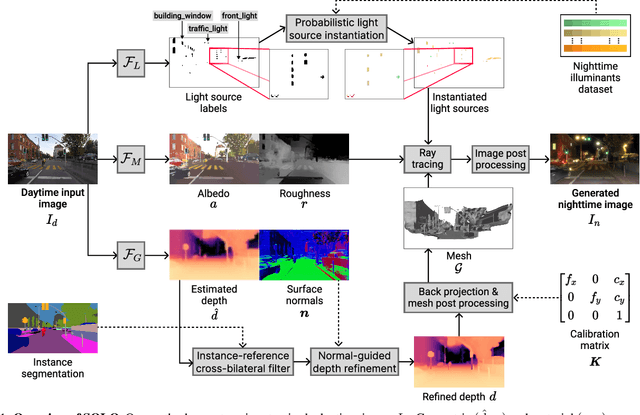



Nighttime scenes are hard to semantically perceive with learned models and annotate for humans. Thus, realistic synthetic nighttime data become all the more important for learning robust semantic perception at night, thanks to their accurate and cheap semantic annotations. However, existing data-driven or hand-crafted techniques for generating nighttime images from daytime counterparts suffer from poor realism. The reason is the complex interaction of highly spatially varying nighttime illumination, which differs drastically from its daytime counterpart, with objects of spatially varying materials in the scene, happening in 3D and being very hard to capture with such 2D approaches. The above 3D interaction and illumination shift have proven equally hard to model in the literature, as opposed to other conditions such as fog or rain. Our method, named Sun Off, Lights On (SOLO), is the first to perform nighttime simulation on single images in a photorealistic fashion by operating in 3D. It first explicitly estimates the 3D geometry, the materials and the locations of light sources of the scene from the input daytime image and relights the scene by probabilistically instantiating light sources in a way that accounts for their semantics and then running standard ray tracing. Not only is the visual quality and photorealism of our nighttime images superior to competing approaches including diffusion models, but the former images are also proven more beneficial for semantic nighttime segmentation in day-to-night adaptation. Code and data will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge