Subword-Level Language Identification for Intra-Word Code-Switching
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2019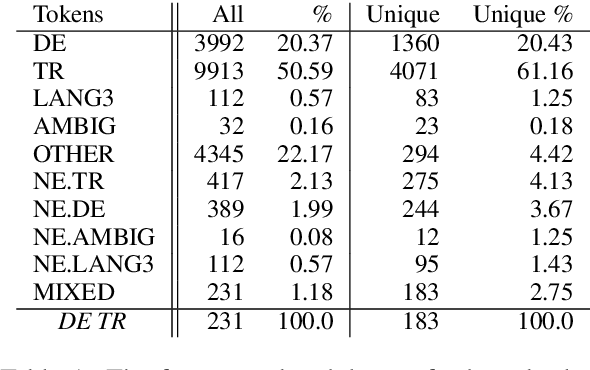

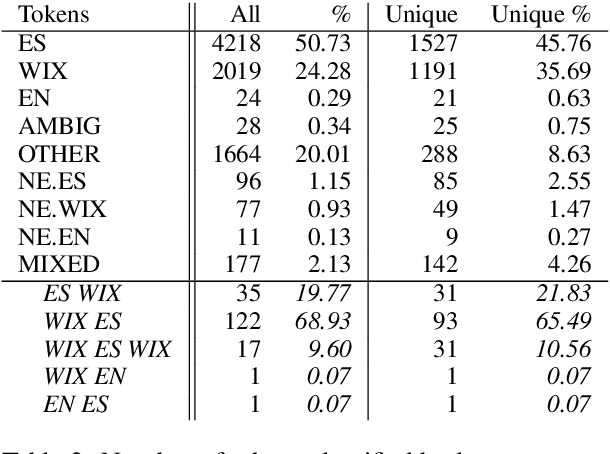
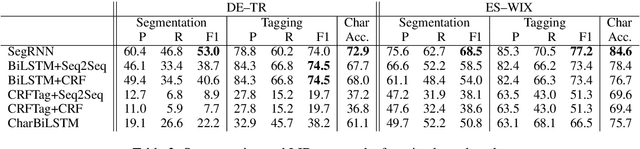
Language identification for code-switching (CS), the phenomenon of alternating between two or more languages in conversations, has traditionally been approached under the assumption of a single language per token. However, if at least one language is morphologically rich, a large number of words can be composed of morphemes from more than one language (intra-word CS). In this paper, we extend the language identification task to the subword-level, such that it includes splitting mixed words while tagging each part with a language ID. We further propose a model for this task, which is based on a segmental recurrent neural network. In experiments on a new Spanish--Wixarika dataset and on an adapted German--Turkish dataset, our proposed model performs slightly better than or roughly on par with our best baseline, respectively. Considering only mixed words, however, it strongly outperforms all baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge