Substitute Based SCODE Word Embeddings in Supervised NLP Tasks
Paper and Code
Jul 25, 2014
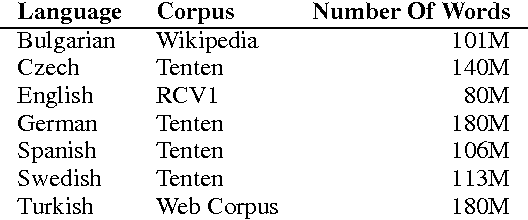
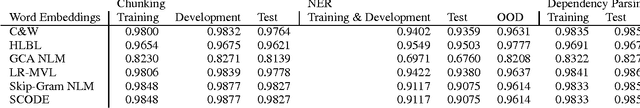

We analyze a word embedding method in supervised tasks. It maps words on a sphere such that words co-occurring in similar contexts lie closely. The similarity of contexts is measured by the distribution of substitutes that can fill them. We compared word embeddings, including more recent representations, in Named Entity Recognition (NER), Chunking, and Dependency Parsing. We examine our framework in multilingual dependency parsing as well. The results show that the proposed method achieves as good as or better results compared to the other word embeddings in the tasks we investigate. It achieves state-of-the-art results in multilingual dependency parsing. Word embeddings in 7 languages are available for public use.
* 11 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge