Studying the Similarity of COVID-19 Sounds based on Correlation Analysis of MFCC
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2020
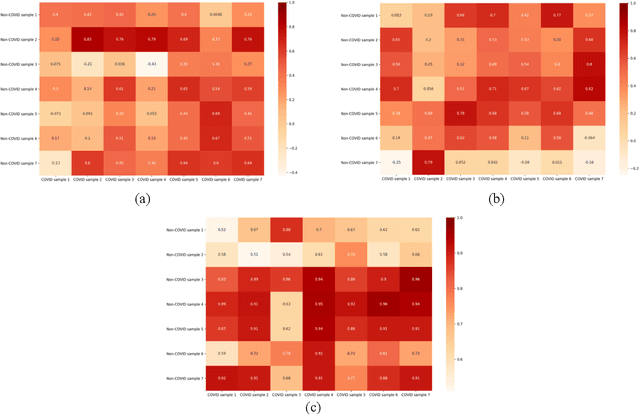

Recently there has been a formidable work which has been put up from the people who are working in the frontlines such as hospitals, clinics, and labs alongside researchers and scientists who are also putting tremendous efforts in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic. Due to the preposterous spread of the virus, the integration of the artificial intelligence has taken a considerable part in the health sector, by implementing the fundamentals of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and deep learning algorithms. In this paper, we illustrate the importance of speech signal processing in the extraction of the Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) of the COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 samples and find their relationship using Pearson correlation coefficients. Our results show high similarity in MFCCs between different COVID-19 cough and breathing sounds, while MFCC of voice is more robust between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 samples. Moreover, our results are preliminary, and there is a possibility to exclude the voices of COVID-19 patients from further processing in diagnosing the disease.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge