Stride: a flexible platform for high-performance ultrasound computed tomography
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2021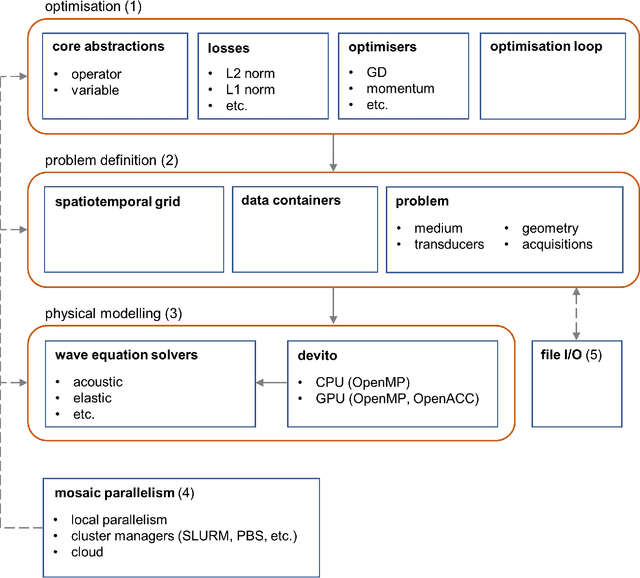
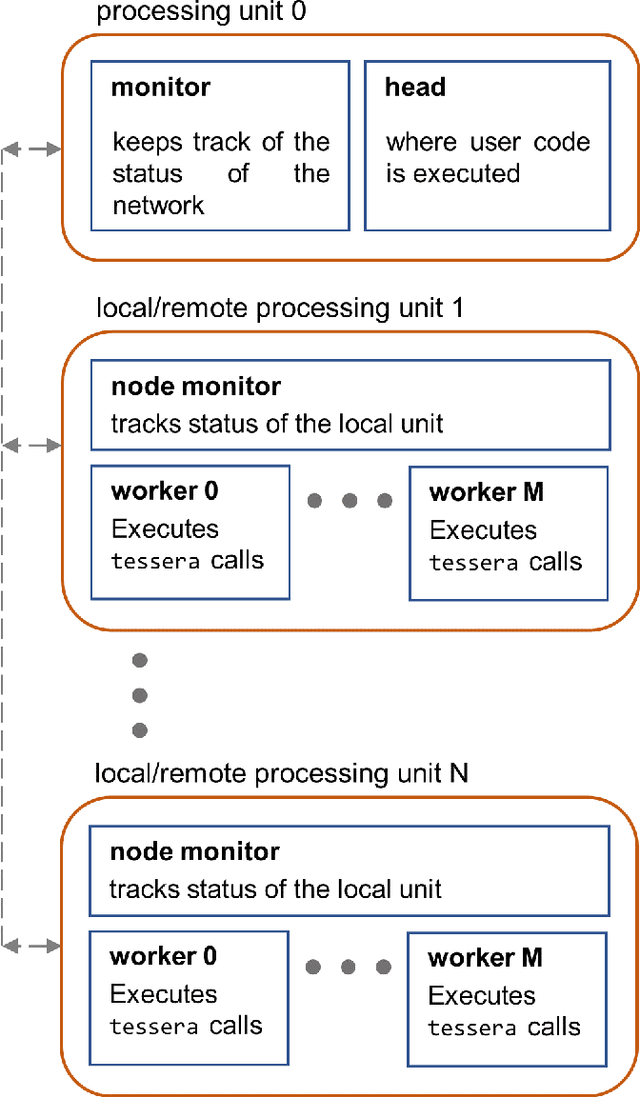
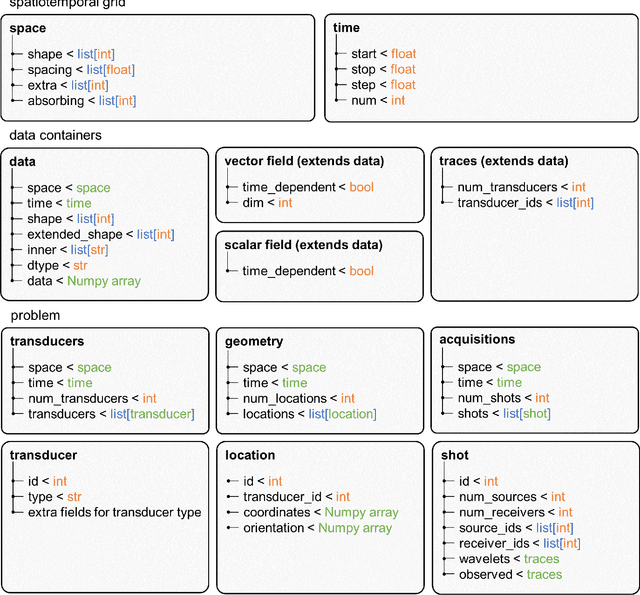
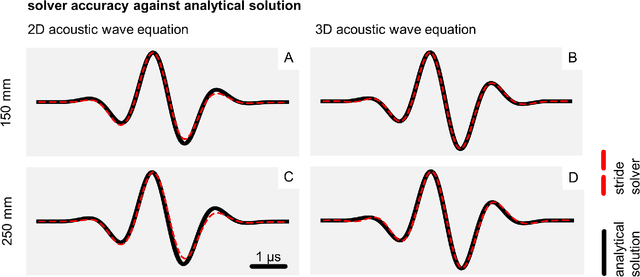
Advanced ultrasound computed tomography techniques like full-waveform inversion are mathematically challenging and orders of magnitude more computationally expensive than conventional ultrasound imaging methods. This computational and algorithmic complexity, and a lack of open-source libraries in this field, represent a barrier preventing the generalised adoption of these techniques, slowing the pace of research and hindering reproducibility. Consequently, we have developed Stride, an open-source Python library for the solution of large-scale ultrasound tomography problems. On one hand, Stride provides high-level interfaces and tools for expressing the types of optimisation problems encountered in medical ultrasound tomography. On the other, these high-level abstractions seamlessly integrate with high-performance wave-equation solvers and with scalable parallelisation routines. The wave-equation solvers are generated automatically using Devito, a domain specific language, and the parallelisation routines are provided through the custom actor-based library Mosaic. Through a series of examples, we show how Stride can handle realistic tomographic problems, in 2D and 3D, providing intuitive and flexible interfaces that scale from a local multi-processing environment to a multi-node high-performance cluster.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge