Steerable Anatomical Shape Synthesis with Implicit Neural Representations
Paper and Code
Apr 04, 2025
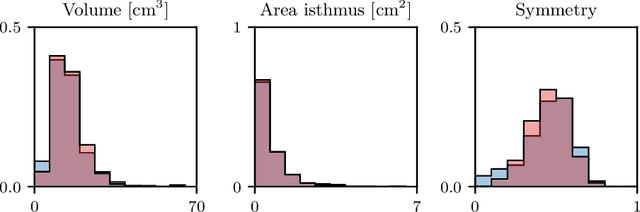
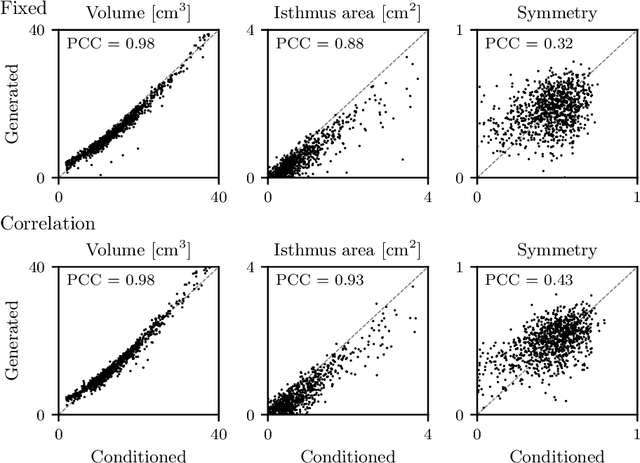
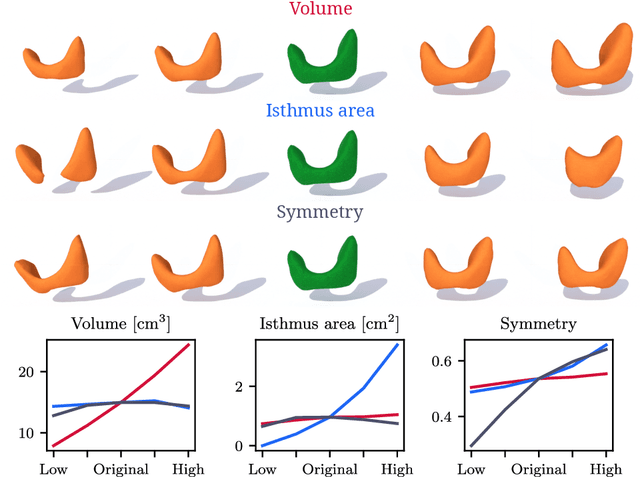
Generative modeling of anatomical structures plays a crucial role in virtual imaging trials, which allow researchers to perform studies without the costs and constraints inherent to in vivo and phantom studies. For clinical relevance, generative models should allow targeted control to simulate specific patient populations rather than relying on purely random sampling. In this work, we propose a steerable generative model based on implicit neural representations. Implicit neural representations naturally support topology changes, making them well-suited for anatomical structures with varying topology, such as the thyroid. Our model learns a disentangled latent representation, enabling fine-grained control over shape variations. Evaluation includes reconstruction accuracy and anatomical plausibility. Our results demonstrate that the proposed model achieves high-quality shape generation while enabling targeted anatomical modifications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge