STEAM & MoSAFE: SOTIF Error-and-Failure Model & Analysis for AI-Enabled Driving Automation
Paper and Code
Dec 15, 2023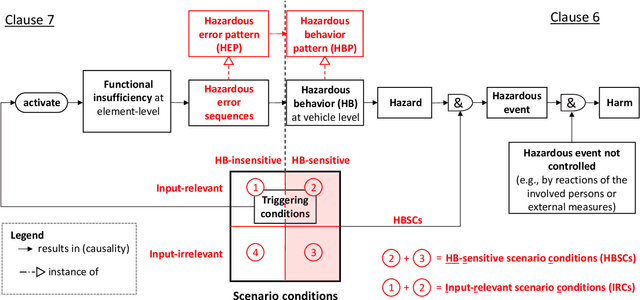
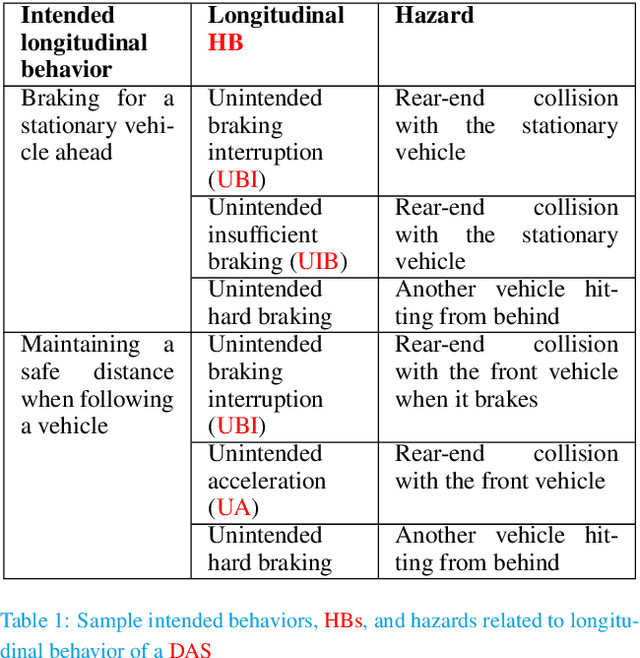
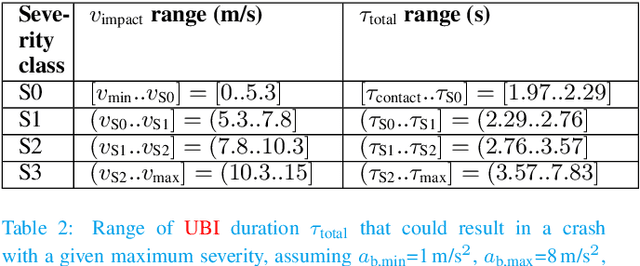
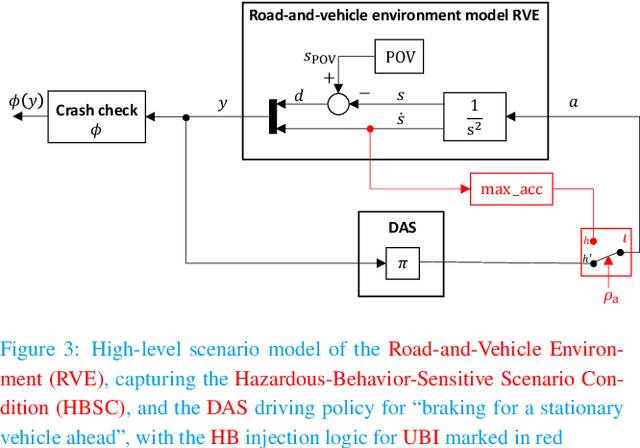
Driving Automation Systems (DAS) are subject to complex road environments and vehicle behaviors and increasingly rely on sophisticated sensors and Artificial Intelligence (AI). These properties give rise to unique safety faults stemming from specification insufficiencies and technological performance limitations, where sensors and AI introduce errors that vary in magnitude and temporal patterns, posing potential safety risks. The Safety of the Intended Functionality (SOTIF) standard emerges as a promising framework for addressing these concerns, focusing on scenario-based analysis to identify hazardous behaviors and their causes. Although the current standard provides a basic cause-and-effect model and high-level process guidance, it lacks concepts required to identify and evaluate hazardous errors, especially within the context of AI. This paper introduces two key contributions to bridge this gap. First, it defines the SOTIF Temporal Error and Failure Model (STEAM) as a refinement of the SOTIF cause-and-effect model, offering a comprehensive system-design perspective. STEAM refines error definitions, introduces error sequences, and classifies them as error sequence patterns, providing particular relevance to systems employing advanced sensors and AI. Second, this paper proposes the Model-based SOTIF Analysis of Failures and Errors (MoSAFE) method, which allows instantiating STEAM based on system-design models by deriving hazardous error sequence patterns at module level from hazardous behaviors at vehicle level via weakest precondition reasoning. Finally, the paper presents a case study centered on an automated speed-control feature, illustrating the practical applicability of the refined model and the MoSAFE method in addressing complex safety challenges in DAS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge