Statistical Linear Regression Approach to Kalman Filtering and Smoothing under Cyber-Attacks
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2025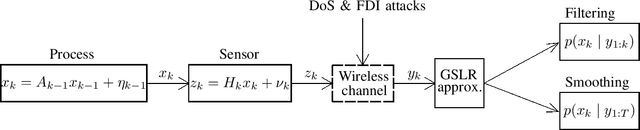
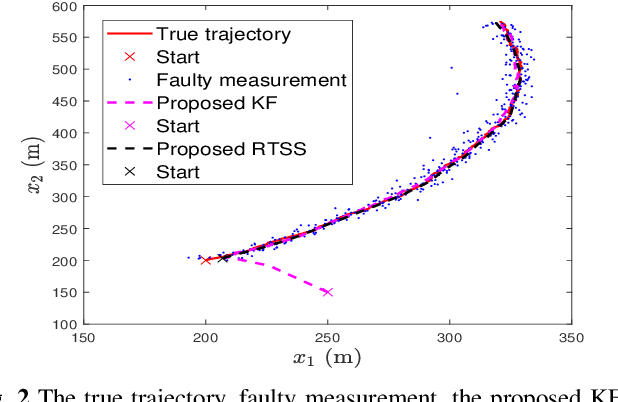
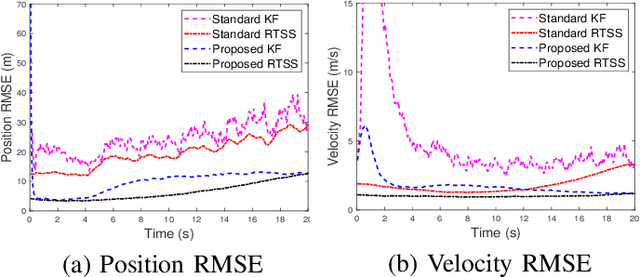
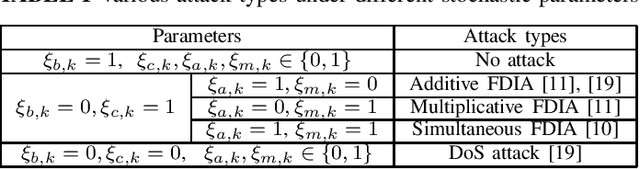
Remote state estimation in cyber-physical systems is often vulnerable to cyber-attacks due to wireless connections between sensors and computing units. In such scenarios, adversaries compromise the system by injecting false data or blocking measurement transmissions via denial-of-service attacks, distorting sensor readings. This paper develops a Kalman filter and Rauch--Tung--Striebel (RTS) smoother for linear stochastic state-space models subject to cyber-attacked measurements. We approximate the faulty measurement model via generalized statistical linear regression (GSLR). The GSLR-based approximated measurement model is then used to develop a Kalman filter and RTS smoother for the problem. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithms under cyber-attacks is demonstrated through a simulated aircraft tracking experiment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge